6.9 Compatible Adjustment Function
6-69
6
Adjustm
e
nts
6.9.4
Proportional Control
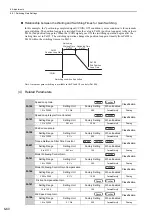
The /P-CON signal can be sent from the host control to select proportional control.
The speed control section uses a PI control if the reference stays zero in the speed control. This integral effect
may cause the servomotor to move. Switch the PI control to a proportional control to prevent this from occur-
ring.
If the speed control is set with a zero clamp function, however, a position loop will be formed so there is no
need to use this function. The speed control is set to proportional control if the /P-CON signal is ON.
Proportional control operation is set using parameter Pn000.1 and input signal /P-CON.
(1) /P-CON Input Signal
Input signal /P-CON is used to switch between PI control and P control.
Example: Factory-set Input Signal Allocations
Note: This is an example when the input signal allocations are at the default factory settings.
(2) Control Method and Proportional Control Input Signal
Proportional control operation is enabled when the control method is set to speed or position control.
Note: Refer to
5.7 Combination of Control Methods
for how to switch control methods.
Type
Signal
Name
Connector
Pin Number
Setting
Meaning
Input
/P-CON
CN1-41
[Factory setting]
OFF (High level)
Switches to PI control (proportional-integral
control).
ON (Low level)
Switches to P control (proportional control).
SERVOPACK
/P-CON
P/PI Switching
41
CN1
Analog
Parameter
Contents
Switching to the Proportional
Control
Pn000
n.
0
[Fac-
tory setting]
Speed control
Can be switched with the factory
setting (CN1-41=/P-CON).
/P-CON signal can be allocated to
other terminals as required.
n.
1
Position control
n.
2
Torque control
Cannot switch to proportional
control.
n.
3
Internal set speed control
Allocation of /P-CON to one of
terminals CN1-40 to 46 are
needed.
n.
4
Internal set speed control
⇔
Speed control
n.
5
Internal set speed control
⇔
Position control
n.
6
Internal set speed control
⇔
Torque control
n.
7
Position control
⇔
Speed control
n.
8
Position control
⇔
Torque control
n.
9
Torque control
⇔
Speed control
n.
A
Speed control
⇔
Speed control with zero clamp
function
n.
B
Position control
⇔
Position control with reference
pulse inhibit function