TOBY-L4 series - System Integration Manual
UBX-16024839 - R04
Design-in
Page 72 of 143
o
Radiation performance depends on the whole PCB and antenna system design, including product
mechanical design and usage. Antennas should be selected with optimal radiating performance in the
operating bands according to the mechanical specifications of the PCB and the whole product.
o
It is recommended to select a pair of custom antennas designed by an antennas’ manufacturer if the
required ground plane dimensions are very small (e.g. less than 6.5 cm long and 4 cm wide). The
antenna design process should begin at the start of the whole product design process.
o
It is highly recommended to strictly follow the detailed and specific guidelines provided by the antenna
manufacturer regarding correct installation and deployment of the antenna system, including PCB layout
and matching circuitry.
o
Further to the custom PCB and product restrictions, antennas may require tuning to obtain the required
performance for compliance with all the applicable required certification schemes. It is recommended to
consult the antenna manufacturer for the design-in guidelines for antenna matching relative to the
custom application.
In both cases, selecting external or internal antennas, these recommendations should be observed:
Select antennas providing optimal return loss (or VSWR) figures over all the operating frequencies.
Select antennas providing optimal efficiency figures over all the operating frequencies.
Select antennas providing similar efficiency for both the primary (
ANT1
) and the secondary (
ANT2
) antenna.
Select antennas providing appropriate gain figures (i.e. combined antenna directivity and efficiency figures)
so that the electromagnetic field radiation intensity does not exceed the regulatory limits specified in certain
countries (e.g. by the FCC in the United States).
Select antennas capable of providing a low Envelope Correlation Coefficient between the primary (
ANT1
)
and the secondary (
ANT2
) antenna: the 3D antenna radiation patterns should have lobes in different
directions.
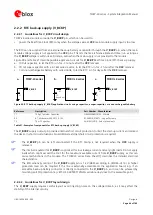
2.4.1.2
Guidelines for antenna RF interface design
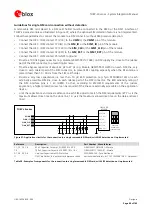
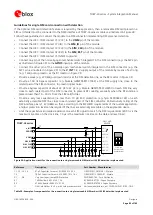
Guidelines for ANT1 / ANT2 pins RF connection design
Correct transition between the
ANT1
/
ANT2
pads and the application board PCB must be provided,
implementing the following design-in guidelines for the application PCB layout close to the
ANT1
/
ANT2
pads:
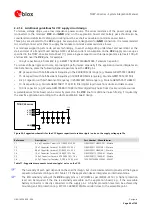
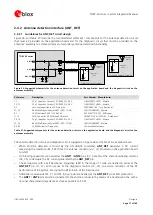
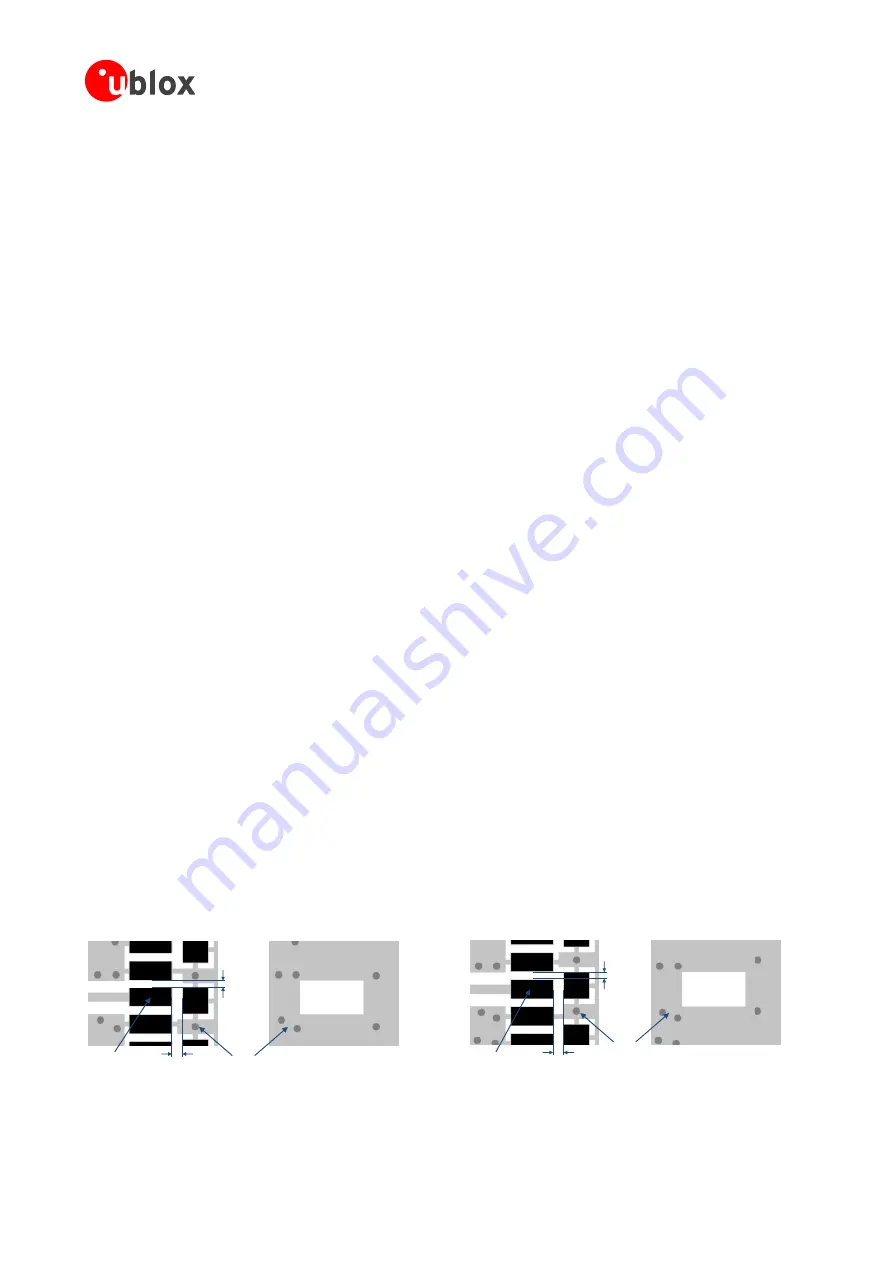
On a multilayer board, the whole layer stack below the RF connection should be free of digital lines.
Increase GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) around the
ANT1
/
ANT2
pads, on the top layer of the
application PCB, to at least 250 µm up to the adjacent pads metal definition and up to 400 µm on the area
below the module, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground, as illustrated in the left example of Figure 32.
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on the buried metal layer below the
ANT1
/
ANT2
pads if
the top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below 200 µm, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground,
as illustrated in the right example of Figure 32.
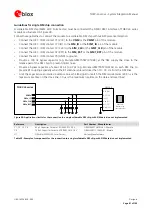
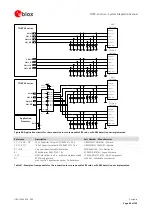
Min.
250 µm
Min. 400 µm
GND
ANT1
GND clearance
on very close buried layer
below ANT1 pad
GND clearance
on top layer
around ANT1 pad
Min.
250 µm
Min. 400 µm
GND
ANT2
GND clearance
on very close buried layer
below ANT2 pad
GND clearance
on top layer
around ANT2 pad
Figure 32: GND keep-out area on top layer around ANT1 / ANT2 pads and on very close buried layer below ANT1 / ANT2 pads