TOBY-L4 series - System Integration Manual
UBX-16024839 - R04
Design-in
Page 110 of 143
2.8.1.3
Guidelines for analog audio layout design
Accurate design of the analog audio circuit is very important to obtain clear and high quality audio. The GSM
signal burst has a repetition rate of 217 Hz that lies in the audible range. A careful layout is required to reduce
the risk of noise from audio lines due to both
VCC
burst noise coupling and RF detection.
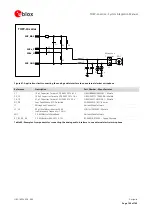
General guidelines for the uplink path (microphone), which is commonly the most sensitive, are the following:
Avoid coupling of any noisy signal to microphone lines: it is strongly recommended to route microphone
lines away from the module
VCC
supply line, any switching regulator line, RF antenna lines, digital lines and
any other possible noise source.
Avoid coupling between the microphone and speaker / receiver lines.
Optimize the mechanical design of the application device, the position, orientation and mechanical fixing
(for example, using rubber gaskets) of microphone and speaker parts in order to avoid echo interference
between the uplink path and downlink path.
Keep ground separation from microphone lines to other noisy signals. Use an intermediate ground layer or
vias wall for coplanar signals.
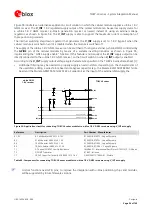
For an external audio device providing differential microphone input, route the microphone signal lines as a
differential pair embedded in ground to reduce differential noise pick-up. The balanced configuration will
help reject the common mode noise.
Cross other signals lines on adjacent layers with 90° crossing.
Place bypass capacitor for RF very close to the active microphone. The preferred microphone should be
designed for GSM applications which typically have an internal built-in bypass capacitor for RF very close to
active device. If the integrated FET detects the RF burst, the resulting DC level will be in the pass-band of the
audio circuitry and cannot be filtered by any other device.
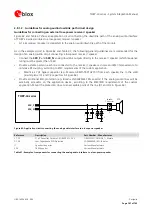
General guidelines for the downlink path (speaker / receiver) are the following:
The physical width of the audio output lines on the application board must be wide enough to minimize
series resistance since the lines are connected to low impedance speaker transducers.
Avoid coupling of any noisy signal to speaker lines: it is recommended to route speaker lines away from the
module
VCC
supply line, any switching regulator line, RF antenna lines, digital lines and any other possible
noise source.
Avoid coupling between speaker / receiver and microphone lines.
Optimize the mechanical design of the application device, the position, orientation and mechanical fixing
(for example, using rubber gaskets) of speaker and microphone parts in order to avoid echo interference
between the downlink path and uplink path.
For external audio device providing differential speaker / receiver output, route the speaker signal lines as a
differential pair embedded in ground up to reduce differential noise pick-up. The balanced configuration will
help reject the common mode noise.
Cross other signals lines on adjacent layers with 90° crossing.
Place the RF bypass capacitor close to the speaker.
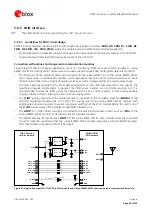
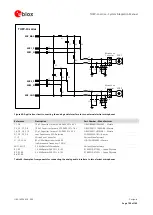
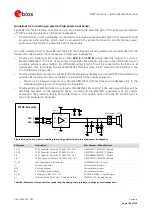
The ESD sensitivity rating of analog audio interface pins is 1 kV (HBM, according to JESD22-A114).
A higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting a general purpose ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to the
accessible points.
If the analog audio pins functionality is not used, they can be left unconnected on the application board.