Guide
to
Electrophysiological
Recording
Guidelines
for
Selecting
a
Headstage
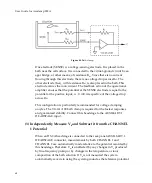
The
H
value
required
depends
on
the
typical
input
resistances,
R
in
,
of
your
cells.
The
recommended
values
given
in
Table
2
are
for
micropipettes.
When
patch
pipettes
are
used,
H
=
0.1
should
be
selected
as
a
matter
of
course.
Some
overlap
in
these
recommendations
is
allowable.
The
guiding
principles
are
these:
H = ×10
for 200 k
Ω
<
R
in
< 5
H = ×1
for 2 M
Ω
<
R
in
< 50
H = ×0.1
for 20 M
Ω
<
R
in
< 500
Table
2.
Recommended
H
values
for
various
cell
input
resistances.
1.
For
maximum
sampling
rates
in
dSEVC
and
DCC
modes
use
the
largest
feasible
H
value.
(This
is
because
the
current
‐
passing
response
is
best
with
low
values
of
R
0
.)
2.
A
limitation
on
using
large
H
values
is
that
as
R
0
becomes
smaller
the
input
leakage
current
of
the
headstage
becomes
more
prone
to
increase
with
time
and
temperature
(see
the
discussion
of
Input
Leakage
Current
later
in
this
section).
3.
A
further
limitation
on
using
large
H
values
is
that
if
R
0
is
less
than
the
microelectrode
resistance,
R
e
,
the
high
‐
frequency
noise
is
worse.
4.
The
H
value
sets
the
current
‐
passing
sensitivity
in
Bridge
and
DCC
modes
and
the
Gain
in
SEVC
modes.
Hence
it
should
be
chosen
for
sensitivities
suitable
for
your
cell.
These
sensitivities
are
listed
in
Table
2
above.
5.
If
R
e
>>
R
in
a
smaller
H
value
should
be
favored.
75