Section 4 - MultiLogger Configuration
46
MLGPS-P
User's Guide
Configuring Rover Solutions
Solutions
are a method of increasing accuracy of positioning by averaging all the readings recorded within a
given interval to receive a more accurate average coordinate for that period. Each solution results in average
3D positional coordinates (Easting, Northing and Height). Longer processing time means higher accuracy
.
For
that reason, the user can create multiple solutions for every baseline, each with a different processing interval.
There is no limit to the number of solutions that can be configured for each Rover or each baseline.
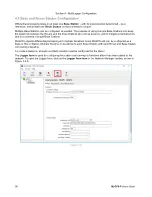
Rover Stations using Differential GPS use
Static
type solutions. The baseline's Base Station must be selected,
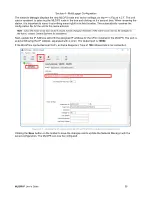
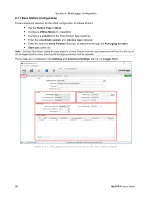
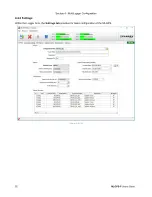
and the solution will then be processed using that Base Station's positional data. Figure 4.3.1 C shows a Rover
with 6 solutions configured, three for each of its two base stations:
(Figure 4.3.2 C)
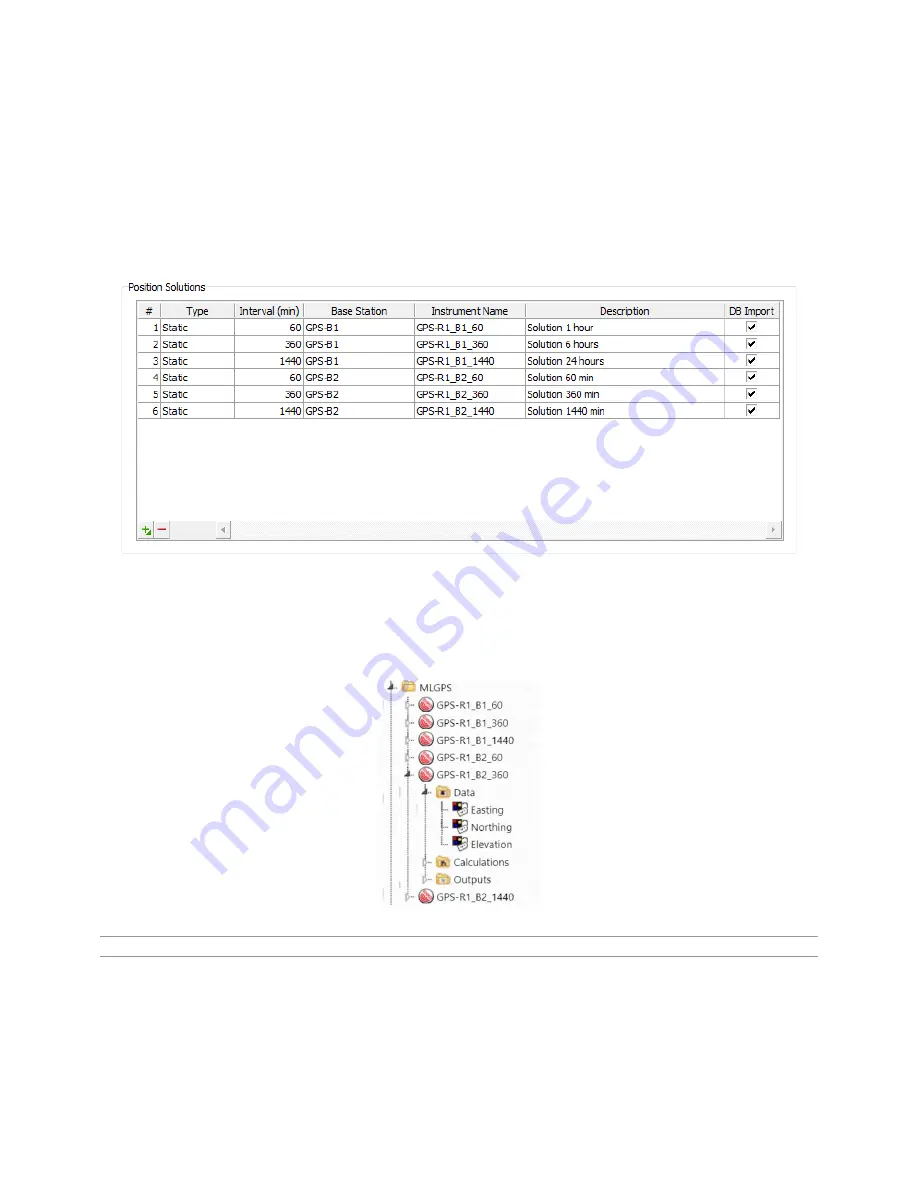
Each solution is imported to the database as an Instrument with three positional Data Elements: Easting,
Northing and Height. Because each solution applies to only one Rover and one baseline, it is important to
establish a naming convention in which solutions can be differentiated. In Figure 4.3.2 C, the example Rover's
solutions contain the Rover name, Base Station name and processing interval, as can be seen in the
Instrument Name
column.
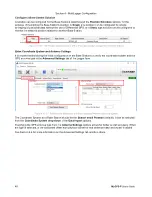
(Figure 4.3.2 D ‒ The solutions from Figure 4.3.2 C in the MLWeb Database Tree, imported as Instruments)
Note
‒ Solutions are not intended to be changed on a regular basis, as this may introduce offsets or shifts in the data.
See
Section 4.4
for detailed information on configuring and working with solutions.