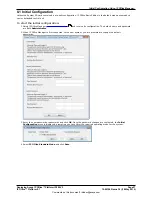
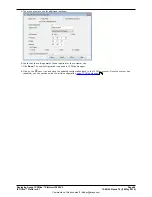
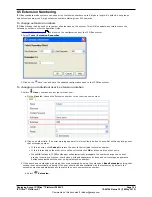
Deploying Avaya IP Office™ Platform IP500 V2
Page 106
15-601042 Issue 30j (18 May 2015)
IP Office™ Platform 9.1
Comments on this document? [email protected]
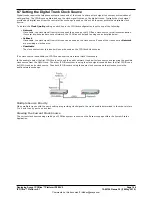
8.7 Setting the Digital Trunk Clock Source
Digital trunks require the telephone system at each end of the trunk to share a clock signal to ensure synchronization of
call signalling. The IP Office can obtain and use the clock signal from any of its digital trunks. Typically the clock signal
provided by a digital trunk from the central office exchange is used as this will be the most accurate and reliable clock
source.
To do this, the Clock Quality setting on each line in the IP Office configuration is set to one of the following:
·
Network
If available, the clock signal from this trunk should be used as the IP Office's clock source for call synchronization.
If several trunk sources are set as Network, the IP Office will default to using one as detailed below.
·
Fallback
If available, the clock signal from this trunk can be used as the clock source if none of the trunks set as Network
are providing a clock source.
·
Unsuitable
The clock source from this trunk will never be used as the IP Office's clock source.
If no clock source is available the IP Office can use its own internal clock if necessary.
In the example below the first IP Office is set to use the public network trunk as its clock source and ignoring the possible
clock source from the QSIG trunk. The other IP Office system is using the clock signal received from the first IP Office on
its QSIG trunk as its clock source. Thus both IP Offices are using the same clock source and that clock source is the
public network exchange.
Multiple Source Priority
When multiple trunks with the same setting are providing clock signals, the trunk used is determined in the order of slots
1 to 4 and then by port on each slot.
Viewing the Current Clock Source
The current clock source being used by an IP Office system is shown on the Resources page within the System Status
Application.