System Control
ARM DDI 0500D
Copyright © 2013-2014 ARM. All rights reserved.
4-249
ID021414
Non-Confidential
on page 4-104Table 4-225
shows the IFAR bit assignments.
To access the IFAR:
MRC p15, 0, <Rt>, c6, c0, 2; Read IFAR into Rt
MCR p15, 0, <Rt>, c6, c0, 2; Write Rt to IFAR
4.5.57
Hyp Data Fault Address Register
The HDFAR characteristics are:
Purpose
Holds the virtual address of the faulting address that caused a synchronous
Data Abort exception that is taken to Hyp mode.
Usage constraints
This register is accessible as follows:
An execution in a Non-secure EL1 state, or in Secure state, makes the
HDFAR
UNKNOWN
.
Configurations
HDFAR is architecturally mapped to AArch64 register FAR_EL2[31:0]
when EL3 is AArch64. See
Fault Address Register, EL2
on page 4-104
.
HDFAR (S) is architecturally mapped to AArch32 register DFAR (S). See
Data Fault Address Register
on page 4-247
.
Attributes
HDFAR is a 32-bit register.
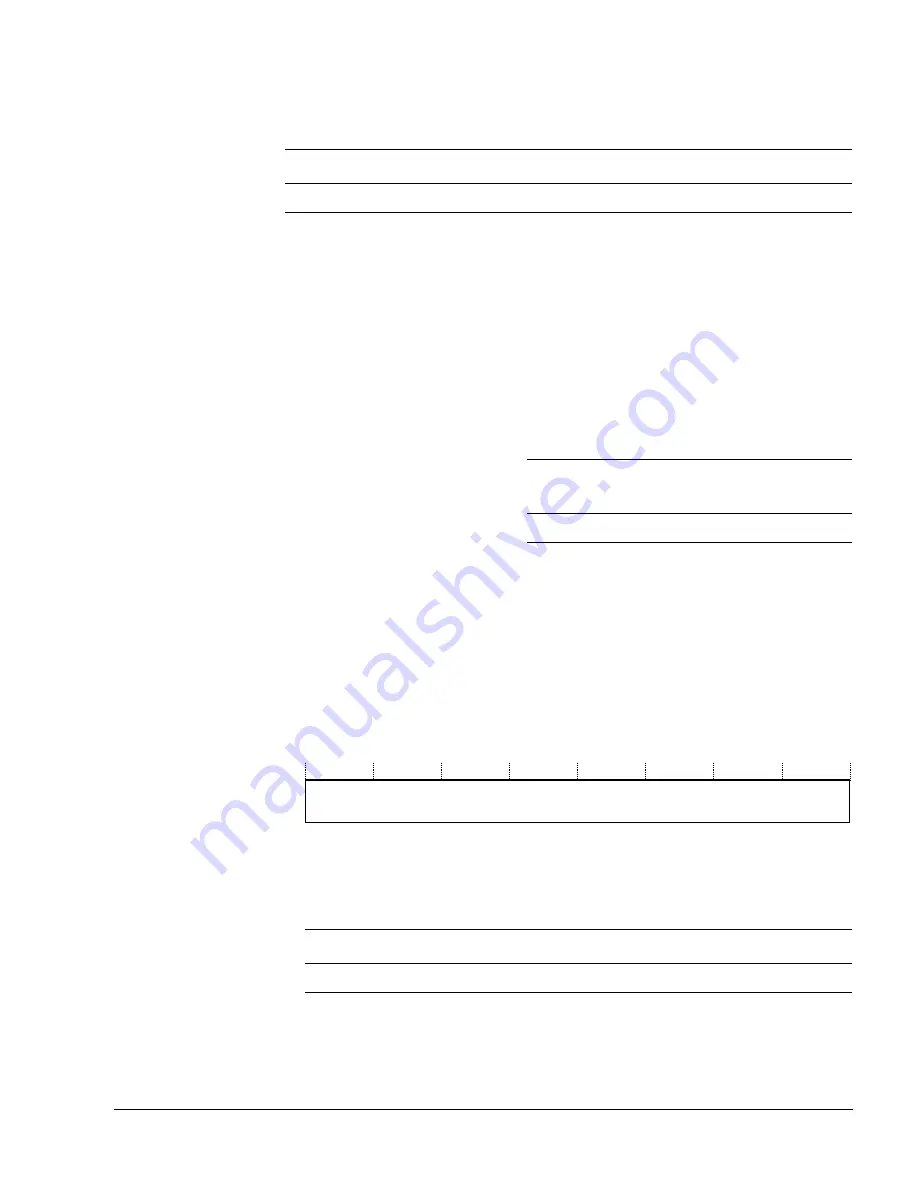
Figure 4-128
shows the HDFAR bit assignments.
Figure 4-128 HDFAR bit assignments
on page 4-104Table 4-226
shows the HDFAR bit assignments.
To access the HDFAR:
MRC p15, 4, <Rt>, c6, c0, 0 ; Read HDFAR into Rt
MCR p15, 4, <Rt>, c6, c0, 0 ; Write Rt to HDFAR
Table 4-225 IFAR bit assignments
Bits
Name
Function
[31:0]
VA
The Virtual Address of faulting address of synchronous Prefetch Abort exception
EL0
(NS)
EL0
(S)
EL1
(NS)
EL1
(S)
EL2
EL3
(SCR.NS = 1)
-
-
-
RW
RW
-
31
0
VA of faulting address of synchronous Data Abort exception
Table 4-226 HDFAR bit assignments
Bits
Name
Function
[31:0]
VA
The Virtual Address of faulting address of synchronous Data Abort exception
















































