The tank heating capacity is determined by the heat loss from the bunker tank and the desired
temperature increase rate.
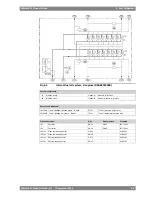
Fig 6-3
Fuel oil viscosity-temperature diagram for determining the pre-heating
temperatures of fuel oils (4V92G0071b)
Example 1:
A fuel oil with a viscosity of 380 cSt (A) at 50°C (B) or 80 cSt at 80°C (C) must be
pre-heated to 115 - 130°C (D-E) before the fuel injection pumps, to 98°C (F) at the separator
and to minimum 40°C (G) in the bunker tanks. The fuel oil may not be pumpable below 36°C
(H).
To obtain temperatures for intermediate viscosities, draw a line from the known
viscosity/temperature point in parallel to the nearest viscosity/temperature line in the diagram.
Example 2:
Known viscosity 60 cSt at 50°C (K). The following can be read along the dotted
line: viscosity at 80°C = 20 cSt, temperature at fuel injection pumps 74 - 87°C, separating
temperature 86°C, minimum bunker tank temperature 28°C.
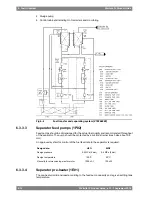
6.3.2
Fuel tanks
The fuel oil is first transferred from the bunker tanks to settling tanks for initial separation of
sludge and water. After centrifuging the fuel oil is transferred to day tanks, from which fuel is
supplied to the engines.
Wärtsilä 32 Product Guide - a21 - 7 September 2016
6-11
6. Fuel Oil System
Wärtsilä 32 Product Guide
Summary of Contents for WARTSILA32
Page 18: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 72: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 130: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 150: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 186: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 204: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 210: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 216: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 238: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 246: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 248: ...This page intentionally left blank...
Page 251: ......
Page 252: ......
Page 253: ......