________________________________________________________________________________
EVO STAR 60-800
18
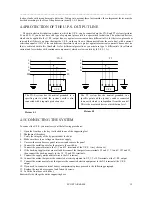
4 CONNECTING THE U.P.S. TO THE MAINS
SUPPLY
CAUTION! : ALL CONNECTING PROCEDURES DESCRIBED IN THIS CHAPTER MUST
BE CARRIED OUT BY AUTHORIZED ELECTRICIANS OR BY QUALIFIED
TECHNICIANS.
CAUTION! : THE U.P.S. NEED A NEUTRAL WIRE. THE SYSTEM CANNOT WORK
WITHOUT IT.
4.1 COMPATIBILITY WITH THE POWER SUPPLY
The parallel connection to the public mains is normally allowed, as the U.P.S. is comparable to a passive charge.
The mains supply must supply a higher power than the U.P.S rated power as it has to take into account several factors,
such as:
1.
Power absorbed by the output charge on the uninterruptible power supply
2.
System efficiency
3.
Power needed to charge the batteries
4.
Input harmonic distortion
If you know the amount of power needed by the connected electrical equipment and you can evaluate the probable
expansion margins it is possible to make a first rough estimate of the power required. As for the power absorbed by the
batteries while charging, you can easily work out the power required by multiplying 436 times 1/10 of the total battery
capacity (E.g.: For a 40A/h battery space, the power needed to charge the battery will be: 436 X (40 / 10) = 1,744 kW).
As for input harmonic distortion please remember that for the power supply the uninterruptible power supply is to be
considered as a non-linear load, which generates harmonic frequency currents multiples of the (50/60 Hz). In function
of the line impedance these create a harmonic voltage distortion. This latter value (total harmonic voltage distortion)
must not exceed the specific environment reference parameters. There are several ways of reducing this parameter: by
increasing the power supply, the section of power supplies cables or by choosing an interruptible power supply with
specific features (twelve-phase input, with filter).
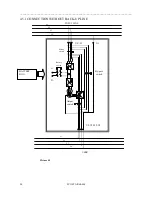
4.2 INDIRECT POWER SUPPLY
4.2.1 TRANSFORMER
If you are using a system input isolation transformer this will reduce distortion effects and stop its diffusion in the
system. Therefore, apart from decreasing harmonic disturbance you can also probably avoid oversizing the power
supply line.
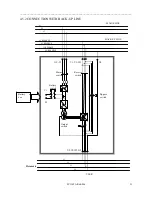
4.2.2 GENERATOR
Particular attention must be paid when sizing a possible input power unit; this has high output impedance, which is
defined on the rating plate as subtransient reactance of the alternator. This parameter makes a negligible harmonic
current distortion become a seriously disturbing element for the correct functioning of the U.P.S.
4.3 INPUT WIRE SIZING
When choosing the wire you must bear in mind a technical, economical and safety evaluation. Technically speaking,
the main factors that affect wire sizing are voltage, current, overcurrent, temperature and how the wires are laid.
However, it is always a good rule to size the wires so as the voltage drop on each wire is below 3% of the applied
voltage. Particularly important is the sizing of the neutral wire especially when the U.P.S. is used to power unbalanced