9
4
Parameter Description
Parameter Description
<Setting>
•
The stop signal (please refer to
Chapter 4
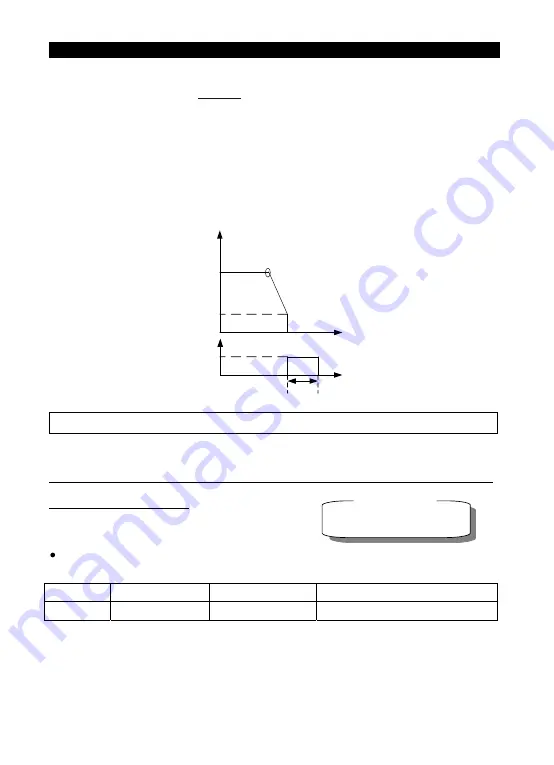
for the primary operation) will cause a gradual decrease
of the output frequency of the inverter. In case the output frequency reaches the DC injection brake
operation frequency (P.10), the DC injection brake will be activated.
•
During DC injection brake, a DC voltage will be injected into the motor windings by the inverter,
which is used to lock the motor rotor. This voltage is called DC injection brake voltage (P.12). The
larger the P.12 value is, the higher the DC brake voltage and the stronger the brake capability.
•
The DC brake operation will last for a period (the set value of P.11) to overcome motor inertia. To
achieve an optimum control, P.11 and P.12 should be set properly.
As shown below:
Note: Users must set P.11 and P.12 appropriately in order to obtain the best control characteristics.
5.8 Starting Frequency (P.13)
P.13 “Starting frequency”
When starting the motor, the instant output frequency of the inverter is referred to as the starting
frequency.
Parameter
Factory Setting
Setting Range
Remarks
-
-
-
z
H
0
6
~
0
z
H
5
.
0
3
1
<Setting>
•
The motor will not run if the target frequency of the inverter is lower than the setting value of P.13.
Inputting the motor starting signal will cause an increase of the output frequency from the value of
P.13.
P.12
Time
P.11
Output
frequency
(
Hz
)
P.10
DC
braking
voltage
Time
Stop signal input
Related parameters
P.2
“
Minimum frequency
”
















































