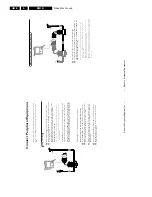
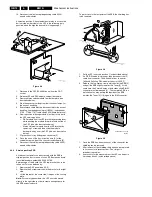
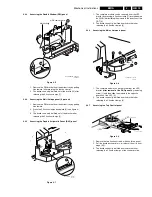
Fault finding and repair tips
GB 21
EM1A
5.
This error is covered by the Flash/Main routine described at
error 7. When during restart the 8 V remains absent, error 5
will be generated.
Error 6
This will occur in the following cases:
–
SCL or SDA is shorted to ground.
–
SCL is shorted to SDA.
–
SDA or SCL connection at the micro controller is open
circuit.
Error 7
Flash detection: From the EHT-info, via D6303 and T7303 a
flash will stop the H-drive and line output stage immediately.
The FLS-bit in the status register of the HOP is set to ‘high’.
As the duration of a flash is very short the FLS-bit will be reset
to ‘low’ again after the flash refresh, so via a slow start the set
will be started again. If this interrupt occurs 5 times within an
interval of 10 seconds (indicating a mains interruption), the
set will go into protection and will generate error 7.
Error 10
Non Volatile Memory (EEPROM - pos. 7012) does not
respond to the micro controller.
Error 11
During the last start-up, the NVM and the micro controller did
not recognise each other (e.g. one of them was replaced or
the NVM memory has been changed/adapted or lost),
therefore the NVM was loaded with default values.
Error 12
Microprocessor (Painter - pos. 7001) internal RAM test
failure.
Error 13
Tuner (pos. 1200) is corrupted, the I
2
C line to the tuner is low,
or there is no supply voltage at pins 7, 4 and 5 of the tuner.
Error 14
Sound controller MSP34xx (pos. 7651) does not respond to
the micro controller.
Error 15
SRAM test failure (pos. 7011).
Error 16
The Tuner (pos. 7201) on the PIP/DW-panel does not
respond to the micro controller.
Error 17
Multi PIP IC SAB9081 I
2
C communication failure (pos. 7801
on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 18
I/O expander IC M62320P I
2
C communication failure (pos.
7403 on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 23
BOCMA IC TDA888xx I
2
C communication failure (pos. 7301
on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 27
Virtual Dolby IC error.
Error 30
TDA 9320 HIP I/O-video processing (pos. 7323 on the SSB).
Error 31
SAA4978 PICNIC error (pos. 7709 on the SSB).
Error 32
TDA 9330 HOP video control/geometry error (pos. 7301 on
the SSB).
Note:
Error codes 1, 2 and 4 are protection codes and in this case
supplies of some circuits will be switched off. Also in
protection, the LED will blink the number of times equivalent
to the most recent error code.
5.6
The 'blinking LED' procedure
The contents of the error buffer can also be made visible
through the 'blinking LED' procedure. This is especially
useful when there is no picture.
When the SDM is entered, the LED will blink the contents of
the error-buffer. Error-codes
≥
10 are shown as follows. A
long blink of 750 msec. which is an indication of the decimal
digit, followed by a pause of 1500 msec, followed by n short
blinks. When all the error-codes are displayed, the sequence
is finished with a LED display of 3 seconds. Then the
sequence starts again.
Example:
Error code position 1 2 3 4 5
Error buffer:
12 9 6 0 0
After entering SDM: 1 long blink (750 ms.) - pause (1500 ms.)
- 2 short blinks - pause (3 s.) - 9 short blinks - pause (3 s.) -
6 short blinks - pause (3 s.) - long blink (3 s.) - etc.
Note: If errors 1, 2 or 4 occur, the LED
always gives the last
occurred error, even if the set is NOT in service mode.
5.7
Protections
5.7.1
General
The EM1A has only one microprocessor (Painter) which
remains active during Standby. This because power of the
microprocessor and the memories is coming from the 3V3
supply, which is derived from the 5V Standby-circuitry. So in
both Power-on as in Standby-mode the microprocessor is
connected to this power supply.
If a fault situation is detected an error code will be generated
and if necessary the set will be put in the protection-mode.
The protection-mode is indicated by blinking of the red LED
at a frequency of 3 Hz. In some error cases the
microprocessor does not put the set in the protection-mode.
The error codes of the error buffer can be read via the
service-menu (SAM), the blinking LED procedure or via DST/
ComPair. The DST diagnose functionality will force the set
into the Service-standby, which is alike the usual Standby,
however the microprocessor has to remain in normal
operation completely.
To get a quick diagnosis the EM1A has 3 service-modes
implemented:
•
The Customer Service Mode (CSM).
•
The Service Default Mode (SDM). Start-up of the set in a
predefined way.
•
The Service Alignment Mode (SAM). In this mode items
of the set can be adjusted via a menu and with the help
of test patterns.
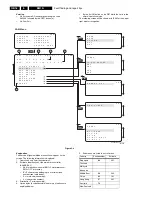
The 'Protection Diagram' shows the structure of the
protection system. See diagram below.