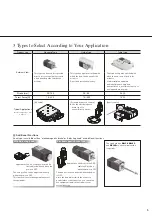
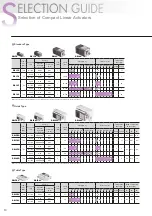
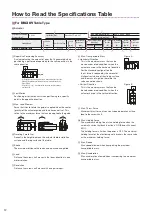
4
[Repetitive Positioning Accuracy]
Ground Ball Screw:
±
0.003
mm
Rolled Ball Screw:
±
0.01
mm
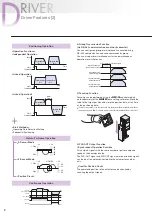
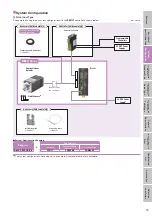
Directly connect the ball screw nut and hollow rotor.
Hollow Rotor
Ball Screw Shaft
Ball Screw Nut
Internal Structure
The
DRL
Series features a structure in which the rotor is
hollowed out and the ball screw is stored inside. The rotation of
the hollow rotor rotates the ball screw nut and by setting up an
anti-spin mechanism
✽
on the tip of the ball screw, the ball screw
shaft is moved in a linear manner.
There are two types of ball screws: the ground ball screw for fine
feed and high-precision positioning and the rolled ball screw
which is reliable for ordinary positioning.
Because the ball screw shaft is stored in the hollow rotor section,
the maximum stroke is secured with the shortest overall length.
Also, a large bore bearing is positioned on the outer
circumference of the ball screw nut in order to directly receive the
large thrust loads generated in linear motion.
✽
Not necessary for the guide type and table type.
Actuator Features
A stepper motor is used
that stops immediately
and without vibration.
The
DRL
Series uses stepper motors.
Because this is a stepper motor, the positioning
precision per step is high and the motor can be
moved forward and back accurately.
Also, since the fine movement of the shaft (called
hunting) does not occur when stopping, the stop
position can be held correctly.
High Positioning Accuracy
The ball screw nut is linked with the hollow rotor.
Through the coupling rigidity and other aspects of parts
combination, the impact of backlash has been minimized,
achieving high-precision positioning.
No hunting.
Load
Accurate positioning.
Stops immediately and completely with no vibration.
Directly connect the ball screw nut
and hollow rotor.
Store the ball screw shaft in the hollow
rotor section and secure the maximum
stroke with the shortest overall length.
Hollow Rotor
Stator
Ball Screw Shaft
Ball Screw Nut
Large Bore Thrust
Bearings Mechanism