2-22 Setup and Operation
Plug and Play boards are dynamic in nature — the system allocates resources to these
boards upon system boot (Table Section 2-11). Some device drivers support this dynamic
board configuration, but some do not.
Device drivers that do not support the dynamic board configuration are also known as
static device drivers. If using a static device driver, you need to permanently associate
resources assigned with a Plug and Play board, instead of relying on the Plug and Play
default. Otherwise, the device driver might not be able to find the board the next time the
system boots.
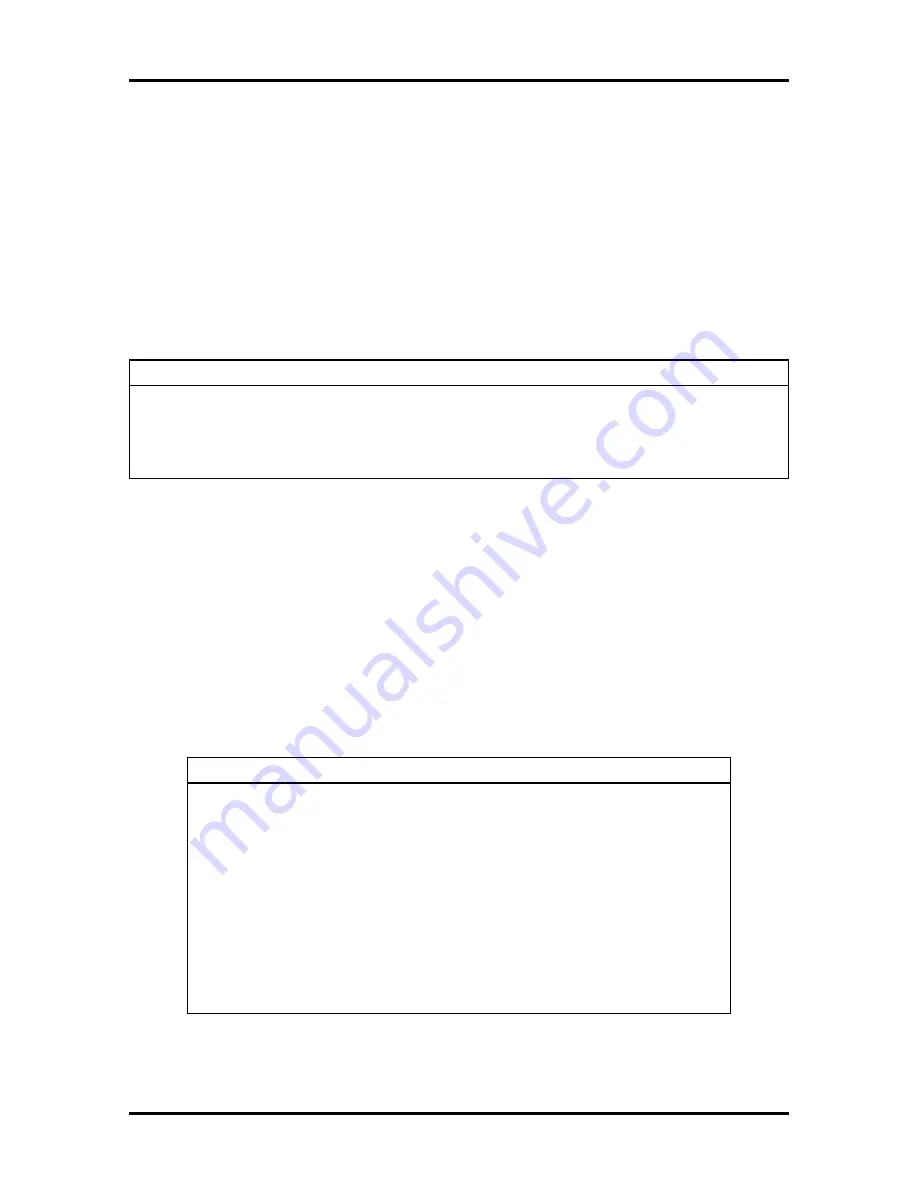
Table Section 2-11 Plug and Play Parameters
Parameter
Options
Description
Plug and Play O/S
Yes
No (default)
Selects the Plug and Play feature which
automatically assigns the address and interrupt for
added options. Functions only for Plug and Play
operating systems.
PCI Device Parameters
Select the PCI Devices parameter if you need to allocate I/O resources (see Table Section
2-12). The combed I/O resource allocation parameter default setting is disabled. The
parameter should be enabled only when a non-plug and play board is not working due to
I/O space resource conflicts. This is particuliarly true for older boards using 10-bit I/O
space decoders rather than the full 16-bit I/O space.
Use the legend keys to make your selections and exit to the main menu.
Table Section 2-12 PCI Device Parameters
Parameter
Options
Description
Combed I/O
Resource Allocation
Enable
Disable
If Enabled, PCI devices requesting I/O
resources are checked: for requests less
than or equal to 256 bytes, that actual I/O
resources are allocated in the first 256
bytes of a 1 KB block of I/O addresses,
and that all PCI to PCI bridges (PPB) have
their ISA Enable bits set.
Note that the BIOS enables Combed I/O
Resource Allocation if it finds a
configurable PCI VGA downstream of a
PPB.
















































