13 - 72 WiNG 5.6 Access Point System Reference Guide
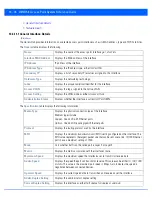
13.3.9 Radios
Access Point Statistics
The
Radio
statistics screens display information on access point radios. The actual number of radios depend on the access point
model and type. This screen displays information on a per radio basis. Use this information to refine and optimize the
performance of each radio and therefore improve network performance.
The access point’s radio statistics screens provide details about associated radios. It provides radio ID, radio type, RF quality
index etc. Use this information to assess the overall health of radio transmissions and access point placement. An AP7131N
model access point can support from 1-3 radios depending on the SKU purchased. AP6532, AP6522, AP6562, AP71xx, AP8132
and AP8232 access points are dual radio models and AP6511 and AP6532 models are both single radio models. An ES6510 is
a controller or service platform managed Ethernet Switch, with no embedded device radios.
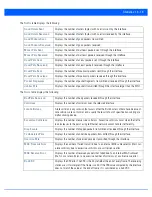
Each of these screens provide enough statistics to troubleshoot issues related to the following three areas:
•
Status
•
RF Statistics
•
Traffic Statistics
Individual access point radios display as selectable links within each of the three access point radio screens. To review a radio’s
configuration in greater detail, select the link within the Radio column of either the
Status
,
RF Statistics
or
Traffic Statistics
screens.
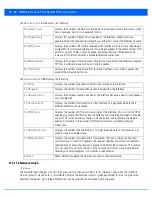
Additionally, navigate the
Traffic
,
WMM TSPEC
,
Wireless LANs
and
Graph
options available on the upper, left-hand side, of
the screen to review radio traffic utilization, WMM QoS settings, WLAN advertisement and radio graph information in greater
detail. This information can help determine whether the radio is properly configured in respect to its intended deployment
objective.
Secondary Next
Hop State
Displays whether the secondary hop is applied to incoming routed packets (UP/UNREACHABLE).
Default Next Hop
IP
If a packet subjected to PBR does not have an explicit route to the destination, the configured
default next hop is used. This is either the IP address of the next hop or the outgoing interface. Only
one default next hop is available. The difference between the next hop and the default next-hop is
in case of former, PBR occurs first, then destination based routing. In case of the latter, the order
is reverse.
Default Next Hop
State
Displays whether the default hop is being applied to incoming routed packets.
Refresh
Select the
Refresh
button to update the screen’s statistics counters to their latest values.
Summary of Contents for WiNG 5.6
Page 1: ...Motorola Solutions WiNG 5 6 ACCESS POINT SYSTEM REFERENCE GUIDE ...
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...8 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 26: ...1 4 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 38: ...2 12 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 74: ...3 36 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 468: ...6 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide Figure 6 1 Configuration Wireless menu ...
Page 568: ...6 102 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 614: ...7 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 660: ...8 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 716: ...9 56 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 730: ...10 14 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 982: ...14 20 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 984: ...A 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1046: ...B 62 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1047: ......