6 - 22 WiNG 5.6 Access Point System Reference Guide
WEP 64 Deployment Considerations
Before defining a WEP 64 supported configuration on a WLAN, refer to the following deployment guideline to ensure the
configuration is optimally effective:
• Motorola Solutions recommends additional layers of security (beyond WEP 64) be enabled to minimize the likelihood of data
loss and security breaches. WEP enabled WLANs should be mapped to an isolated VLAN with Firewall policies restricting
access to hosts and suspicious network applications.
6.1.2.11 WEP 128 and KeyGuard
Configuring WLAN Security
Wired Equivalent Privacy
(WEP) is a security protocol specified in the IEEE
Wireless Fidelity
(Wi -Fi) standard. WEP is designed
to provide a WLAN with a level of security and privacy comparable to that of a wired LAN.
KeyGuard is a Motorola Solutions encryption option used with legacy clients capable of supporting it. It closely resembled WEP
128 in key structure.
WEP can be used with
open
,
shared
,
MAC
and
802.1 X EAP
authentications. WEP is optimal for WLANs supporting legacy
deployments when also used with 802.1X EAP authentication to provide user and device authentication and dynamic WEP key
derivation and periodic key rotation. 802.1X provides authentication for devices and also reduces the risk of a single WEP key
being deciphered. If 802.1X support is not available on the legacy device, MAC authentication should be enabled to provide
device level authentication.
WEP 128 and KeyGuard use a 104 bit key which is concatenated with a 24-bit
initialization vector
(IV) to form the RC4 traffic
key. WEP may be all a small-business user needs for the simple encryption of wireless data. However, networks that require
more security are at risk from a WEP flaw. WEP is only recommended if there are client devices that are incapable of using
higher forms of security. The existing 802.11 standard alone offers administrators no effective method to update keys.
WEP 128 or Keyguard provide a more robust encryption algorithm than WEP 64 by requiring a longer key length and pass key.
Thus, making it harder to hack through the replication of WEP keys.
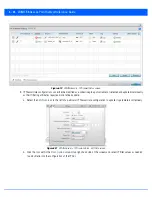
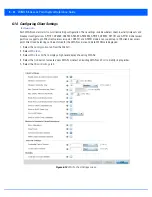
To configure WEP 128 encryption on a WLAN:
1. Select the
Configuration
tab from the Web UI.
2. Select
Wireless.
3. Select
Wireless LANs
to display a high level display of existing WLANs.
4. Select the
Add
button to create an additional WLAN, or select
Edit
to modify the properties of an existing WLAN.
5. Select
Security
.
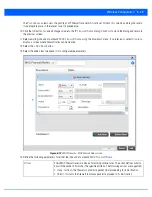
6. Select either the
WEP 128
or
Keyguard
radio button from within the
Select Encryption
field.
The screen populates with the parameters required to define a WEP 128 or KeyGuard configuration for the WLAN.
Summary of Contents for WiNG 5.6
Page 1: ...Motorola Solutions WiNG 5 6 ACCESS POINT SYSTEM REFERENCE GUIDE ...
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...8 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 26: ...1 4 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 38: ...2 12 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 74: ...3 36 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 468: ...6 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide Figure 6 1 Configuration Wireless menu ...
Page 568: ...6 102 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 614: ...7 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 660: ...8 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 716: ...9 56 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 730: ...10 14 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 982: ...14 20 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 984: ...A 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1046: ...B 62 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1047: ......