5 - 296 WiNG 5.6 Access Point System Reference Guide
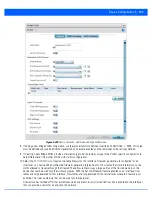
26. Set the following
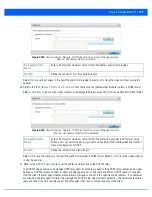
DHCPv6 Client Configuration
. The
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6
(DHCPv6) provides a
framework for passing configuration information.
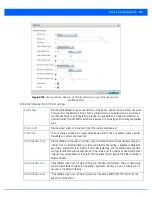
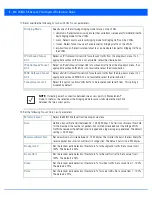
27. Set the following
MTU
settings for the virtual interface:
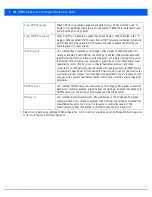
28. Within the
ICMP
field,
define whether ICMPv6 redirect messages are sent. Redirect requests data packets be sent on an
alternative route. This setting is enabled by default.
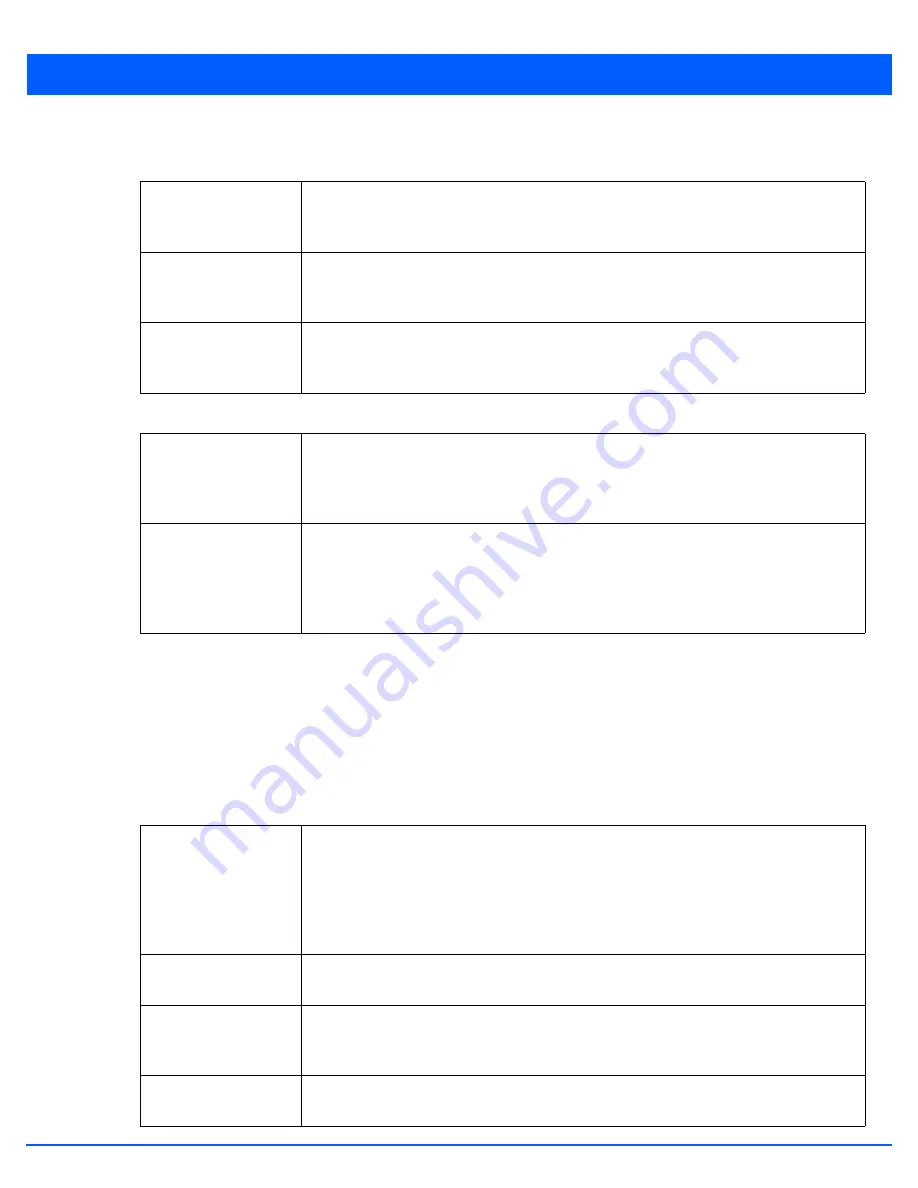
29. Within the
Address Autoconfiguration
field,
define whether to configure IPv6 addresses on this virtual interface based
on the prefixes received in router advertisement messages. Router advertisements contain prefixes used for link
determination, address configuration and maximum hop limits. This setting is enabled by default.
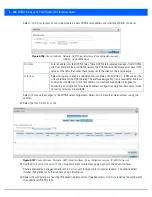
30. Set the following
Router Advertisement Processing
settings for the virtual interface. Router advertisements are
periodically sent to hosts or sent in response to solicitation requests. The advertisement includes IPv6 prefixes and other
subnet and host information.
Stateless DHCPv6
Client
Select this option to request information from the DHCPv6 server using stateless DHCPv6.
DHCPv6 is a networking protocol for configuring IPv6 hosts with IP addresses, IP prefixes or
other configuration attributes required on an IPv6 network. This setting is disabled by default.
Prefix Delegation
Client
Specify a 32 character maximum request prefix for prefix delegation from a DHCPv6 server
over this virtual interface. Devices use prefixes to distinguish destinations that reside on-link
from those reachable using a router.
Request DHCPv6
Options
Select this option to request DHCPv6 options on this virtual interface. DHCPv6 options provide
configuration information for a node that must be booted using the network rather than
locally. This setting is disabled by default.
Maximum
Transmission Unit
(MTU)
Set the PPPoE client
maximum transmission unit
(MTU) from 500 - 1,492. The MTU is the
largest physical packet size in bytes a network can transmit. Any messages larger than the
MTU are divided into smaller packets before being sent. A PPPoE client should be able to
maintain its point-to-point connection for this defined MTU size. The default MTU is 1,492.
IPv6 MTU
Set an IPv6 MTU for this virtual interface from 1,280 - 1,500. A larger MTU provides greater
efficiency because each packet carries more user data while protocol overheads, such as
headers or underlying per-packet delays, remain fixed; the resulting higher efficiency means
a slight improvement in bulk protocol throughput. A larger MTU results in the processing of
fewer packets for the same amount of data. The default is 1,500.
Accept RA
Enable this option to allow router advertisements over this virtual interface. IPv6 hosts can
configure themselves automatically when connected to an IPv6 network using the neighbor
discovery protocol via ICMPv6 router discovery messages. When first connected to a network,
a host sends a link-local router solicitation multicast request for its configuration parameters;
routers respond to such a request with a router advertisement packet that contains Internet
layer configuration parameters.This setting is enabled by default.
No Default Router
Select this option to consider routers unavailable on this interface for default router selection.
This setting is disabled by default.
No MTU
Select this option to not use the existing MTU setting for router advertisements on this virtual
interface. If the value is set to zero no MTU options are sent. This setting is disabled by
default.
No Hop Count
Select this option to not use the hop count advertisement setting for router advertisements
on this virtual interface. This setting is disabled by default.
Summary of Contents for WiNG 5.6
Page 1: ...Motorola Solutions WiNG 5 6 ACCESS POINT SYSTEM REFERENCE GUIDE ...
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...8 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 26: ...1 4 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 38: ...2 12 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 74: ...3 36 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 468: ...6 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide Figure 6 1 Configuration Wireless menu ...
Page 568: ...6 102 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 614: ...7 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 660: ...8 46 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 716: ...9 56 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 730: ...10 14 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 982: ...14 20 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 984: ...A 2 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1046: ...B 62 WiNG 5 6 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1047: ......