Power and Voltage Quality Trainer
AD 2
– MI 3399
132
2.7 Energy measurement
Energy is the generation or use of electric power over a period of time. This is usually
expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
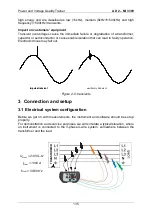
2.8 Harmonics
Any periodic deviation of a pure sinusoidal voltage waveform can be presented with
the sum of sinusoids of the power frequency and its integer multiples. Power frequency
is called the fundamental frequency. A sinusoidal wave with a frequency k times higher
than the fundamental (k is an integer) is called harmonic wave and is denoted with
amplitude and a phase shift (phase angle) to a fundamental frequency signal. The ratio
between harmonic frequency and a fundamental frequency (k) is called harmonic
order.
Origin
Non-linear loads (rectifiers, variable speed drives, fluorescent lamps, PC, TV...) draw
current with a high THDI (highly non-sinusoidal waveform). For analysis purposes,
non-linear loads can be modelled with linear loads and the (current) source of
harmonics. Current harmonics cause a non-sinusoidal voltage drop on the reference
impedance and a distorted voltage at the power supply terminals. Non-linear loads
disturb the supply voltage in such a way that only
odd harmonics
can be detected
with a measurement instrument.
If the load is non-symmetrically controlled, positive and negative half periods of current
differ in shape and rms value causing
even harmonics
and a DC component to arise.
This situation causes saturation and overheating of transformer cores. A significant DC
component can be caused by geomagnetic storms in some areas.
Another source of harmonics is the supply network itself. Magnetisation of the energy
transformer core and its saturation cause non-sinusoidal currents that are manifested
as a THDU on the supply terminals.
Origins of harmonics disturbances
single phase rectifiers
– high 3
rd
harmonic, THDI 80%
three phase loads
– 5
th
, 7
th
, 11
th
, 13
th
, 17
th
harmonic
non-symmetrically controlled supply
– even harmonics and DC
higher pulse number
– lower THDI
serial inductance decreases THDI
LV power supply network
– THDU 1.5 ÷ 4.5%, mainly 5
th
harmonic
Impact on customers’ equipment
overall energy efficiency is decreased
premature ageing of system components
triple harmonics can produce high currents in a neutral line causing overheating
and losses
increased heating, noise and vibrations in transformers and motors
current into capacitor bank increases with harmonic order causing failures
presence of harmonic increase possibility of resonance
problems with signalling frequencies
tripping of protection devices
Summary of Contents for MI 3399
Page 27: ...Electrical Installation Safety Trainer AD 1 MI 3399 27...
Page 46: ...Electrical Installation Safety Trainer AD 1 MI 3399 46 3 Exit settings...
Page 74: ...Electrical Installation Safety Trainer AD 1 MI 3399 74...
Page 197: ...Power and Voltage Quality Trainer AD 2 MI 3399 197 Figure 4 89 Transient Chart view...
Page 204: ...PAT Appliances Machines Safety Trainer AD 3 MI 3399 204...
Page 249: ...PV Photovoltaic Systems Trainer AD 4 MI 3399 249...
Page 250: ...PV Photovoltaic Systems Trainer AD 4 MI 3399 250 AD 4 MI 3399 PV Photovoltaic Systems Trainer...