For our next example relay, consider a three phase, three-wire relay that monitors phase-to-
phase voltage, and two-phase currents. For a balanced load condition the formula
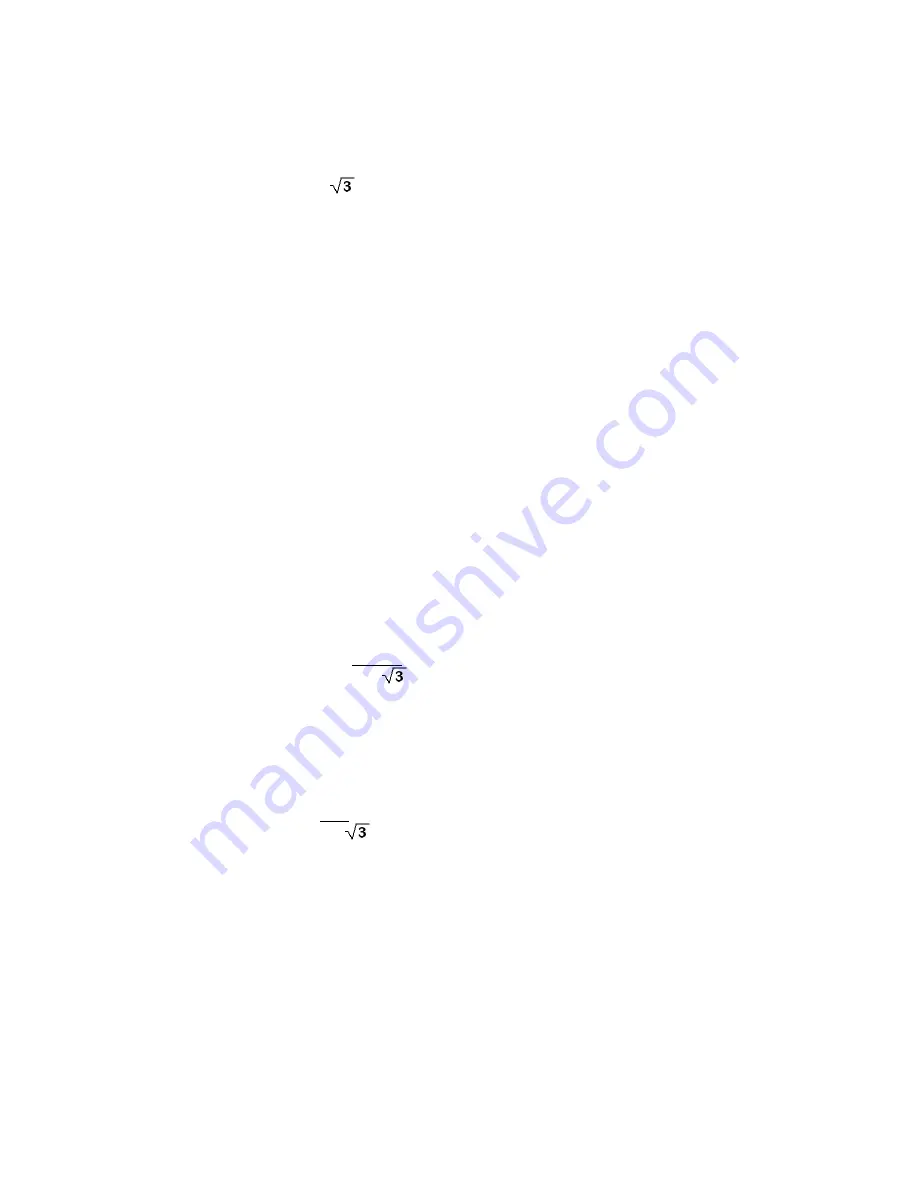
* Voltage
θ
1
-
θ
2
* Current * Cosine
θ
would be used to calculate Watts. In this test case the manufacture recommends testing the
relay using a single-phase voltage and parallel the voltage to the relay potential sensing coils.
Also, a single-phase current is applied in series to the two current input terminals. It should be
noted that in using the manufacturer’s recommended test procedure, the relay is calibrated in
three-phase watts using ½ the pickup current corresponding to the relay pickup in watts using the
previous stated formula. Other three-phase relays may also be tested using a single-phase
voltage and current source. For example, to test a three phase, four-wire, phase-neutral sensing
relay using a single phase voltage and current source requires the use of the following formula to
calculate three-phase watts,
3 * Voltage * Current * Cosine
θ
In this case, the single phase voltage output is connected in parallel to all three potential sensing
inputs on the relay, and the single phase current is connected in series to all three current inputs.
The Voltage applied will be the phase to neutral voltage enter in the
Normal Volt
window. The
phase angle relationship recommended by the manufacture is 0˚. Therefore, If the relay pickup
setting is 1800 Watts, and the relay voltage is 120 Volts, then we would expect the relay to
operate at about 5.0 Amperes,
3 * 120 * 5 * 1 (Cosine 0˚) = 1800 Watts
For our final example relay, consider a loss of excitation relay, connected phase to phase voltage
and single phase current that is calibrated in watts. The formula
Voltage
θ
1
-
θ
2
* Current * Cosine
θ
would be used to calculate Watts. In this test case the manufacture recommends testing the relay
using a single-phase voltage and a single-phase current. The Voltage applied will be the voltage
entered in the
Normal Volt
window. The phase angle relationship recommended by the
manufacture is 60˚. Therefore, if the relay pickup setting is 75 Watts, and the relay voltage is 120
Volts, then if the relay operates at 2.16 Amperes,
120 * 2.16 * (Cosine 60˚) = 74.91 Watts
Relay Type
This setting selects whether the relay is a solid
state or electromechanical relay. If solid state is
selected then there are no available contacts for
the pick-up test. The user must press Stop
when the pick-up LED illuminates.
Test Multiple / Time
These settings determine at what power
multiples the timing test will be performed.
Common test multiples are 2, 4, and 6. The user
enters the desired multiple and the appropriate
operating time for that multiple. For example, if
the relay to be tested has a tap setting of 40
Watts, and the user selects a test multiple of 2.0,
-
97
www
. ElectricalPartManuals
. com
















































