163
Learning Advanced Features
•
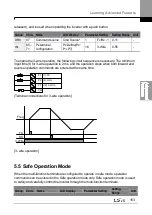
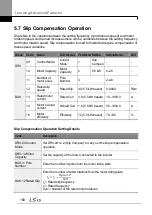
Normal PID output (PID OUT) is bipolar and is limited by PID-46 (PID Limit Hi) and PID-47
(PID Limit Lo) settings. DRV-20 (MaxFreq) value equals a 100% of PID OUT.
•
The following are the variables used in PID operation, and how they are calculated:
-
Unit MAX = PID Unit 100% (PID-68)
-
Unit Min = (2xPID Unit 0% (PID-67)
–PID Unit 100%)
-
Unit Default = (PID Unit 100%-PID Unit 0%)/2
-
Unit Band = Unit 100%-Unit 0%
•
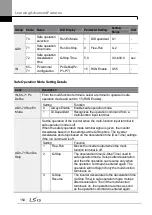
PID control may be utilized for the following operations:
Soft fill, auxiliary PID reference compensation, MMC, flow compensation, pipe breakage
detection
•
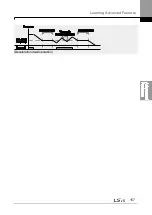
During a PID operation, the PID output becomes the frequency reference. The inverter
accelerates or decelerates to the frequency reference based on the Acc/Dec times.
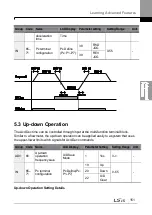
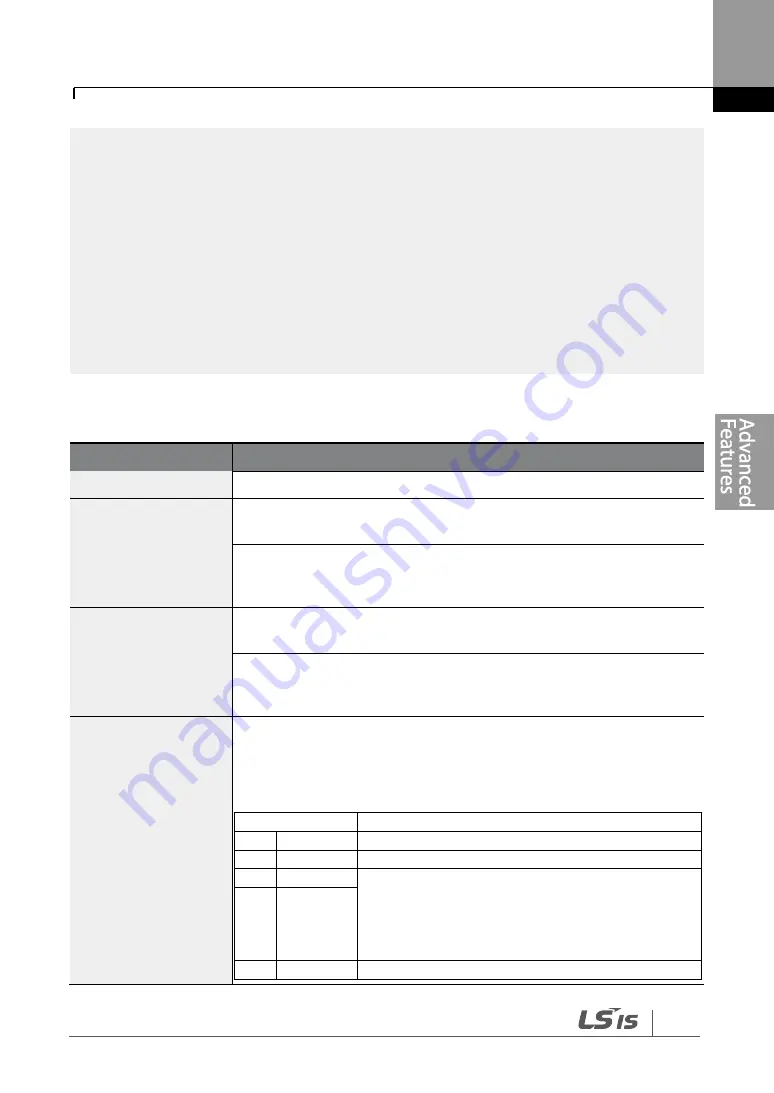
PID Basic Operation Setting Details
Code
Description
PID-01 PID Sel
Sets the code to ‗1 (Yes)‘ to select functions for the process PID.
PID-03 PID Output
Displays the existing output value of the PID controller. The unit, gain,
and scale that were set in the PID group are applied on the display.
PID-04 PID Ref Value
Displays the existing reference value set for the PID controller. The
unit, gain, and scale that were set in the PID group are applied on the
display.
PID-05 PID Fdb Value
Displays the latest feedback value of the PID controller. The unit, gain,
and scale that were set in the PID group are applied on the display.
PID-06 PID Err Value
Displays the differences between the existing reference and the
feedback (error value). The unit, gain, and scale that were set in the
PID group are applied on the display.
PID-10 PID Ref 1 Src
Selects the reference input for the PID control. If the V1 terminal is set
to a PID feedback source (PID F/B Source), the V1 terminal cannot
be set to the PID reference source (PID Ref Source). To set V1 as a
reference source, change the feedback source.
Setting
Function
0
Keypad
Keypad
1
V1
-10-10 V input voltage terminal
3
V2
I2 analog input terminal
When the analog voltage/current input terminal
selection switch (SW4) at the terminal block is set
to I (current), input 0-20 mA current. If it is set to V
(voltage), input 0
–10 V.
4
I2
5
Int. 485
RS-485 input terminal
Summary of Contents for H100
Page 14: ......
Page 18: ...Preparing the Installation 4 37 90 kW 3 Phase ...
Page 27: ...Preparing the Installation 13 ...
Page 47: ...33 Installing the Inverter ...
Page 48: ...Installing the Inverter 34 Input and Output Control Terminal Block Wiring Diagram ...
Page 61: ...47 Installing the Inverter ...
Page 71: ...Learning to Perform Basic Operations 57 ...
Page 88: ...Learning to Perform Basic Operations 74 ...
Page 103: ...89 Learning Basic Features Code Description V1 Quantizing ...
Page 129: ...115 Learning Basic Features ...
Page 140: ...Learning Basic Features 126 ...
Page 148: ...Learning Basic Features 134 ...
Page 171: ...157 Learning Advanced Features Deceleration dwell operation ...
Page 183: ...169 Learning Advanced Features ...
Page 184: ...Learning Advanced Features 170 PID Command Block ...
Page 185: ...171 Learning Advanced Features PID Feedback Block ...
Page 186: ...Learning Advanced Features 172 PID Output Block ...
Page 187: ...173 Learning Advanced Features PID Output Mode Block ...
Page 197: ...183 Learning Advanced Features ...
Page 201: ...187 Learning Advanced Features Code Description 100 EPID1 Control block ...
Page 202: ...Learning Advanced Features 188 EPID2 Control block ...
Page 237: ...223 Learning Advanced Features Time Period Schedule AP3 38 Except3 Day 01 01 ...
Page 244: ...Learning Advanced Features 230 ...
Page 259: ...245 Learning Advanced Features Code Description Code Description Volt ...
Page 362: ...Learning Protection Features 348 ...
Page 415: ...401 RS 485 Communication Features Item Standards Parity check None ...
Page 524: ...Table of Functions 510 ...
Page 533: ...Table of Functions 519 ...
Page 547: ...533 Troubleshooting ...
Page 585: ...Technical Specification 571 ...
Page 594: ...580 ...
Page 595: ...581 ...
Page 596: ...582 ...