Technical data
Page 46
4.5.2
Encoder connector [X2B]
The 15-pin D-SUB connector [X2B] can be used for the feedback of encoder-equipped motors. Possible incremental encoders
for the encoder connector can be divided into several groups. If you want to use other types of encoders, please contact your
sales partner.
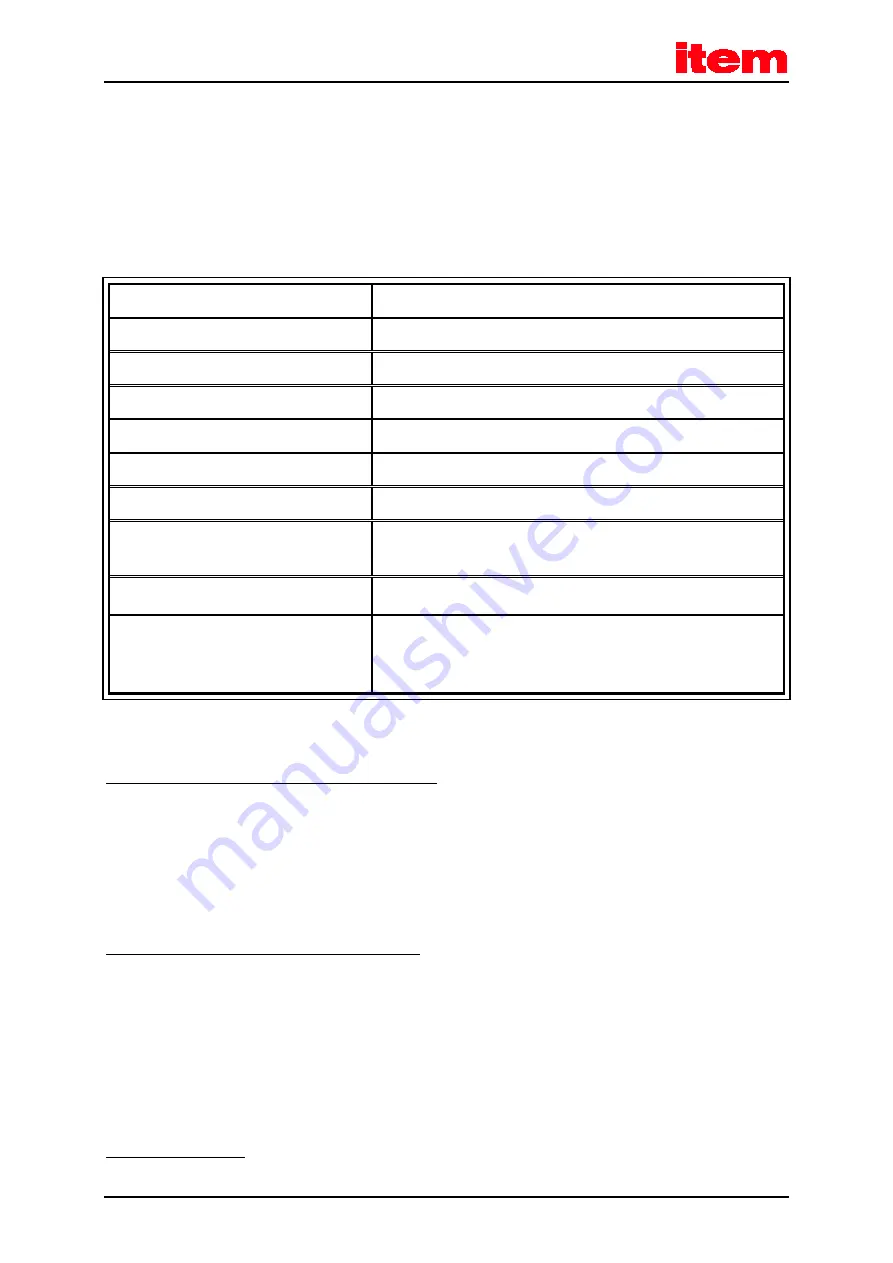
Table 20:
Technical data: encoder evaluation [X2B]
Parameter
Value
Parameterisable number of encoder lines
1 - 2
18
lines/revolution
Angular resolution/interpolation
10 bits/period
Track signals A, B
1 V
PP
differential; 2.5 V offset
Track signals N
0.2 to 1 V
PP
differential; 2.5 V offset
Commutation track A1, B1 (option)
1 V
PP
differential; 2.5 V offset
Track signal input impedance
Differential input 120
Ω
Limit frequency
f
limit
> 300 kHz (high-resolution track)
f
limit
approx.10 kHz (commutation track)
Additional communication interface
EnDat (Heidenhain) and HIPERFACE
®
(Sick-Stegmann)
Supply output
5 V or 12 V; 300 mA max; current-limited
Control via sensor lines
Setpoint programmable via SW
Standard incremental encoders without commutation signals:
This type of encoder is used for low-cost linear motor applications in order to save the costs for the provision of the
commutation signals (Hall sensor). With this type of encoder, the item Servo Positioning Controller C 3-Series must perform an
automatic pole position determination after power-on.
Standard incremental encoders with commutation signals:
This variant uses standard incremental encoders with three additional, binary Hall sensor signals. The line count of the
encoder can be parameterised as desired (1 to 16,384 lines/revolution).
There is an additional offset angle for the Hall sensor signals. It is determined during the motor identification process or it can
be set via the item Motion Soft
parameterisation software. Normally, the Hall sensor offset angle is zero.
Sick-Stegmann encoders:
















































