Function overview
Page 58
5.3.2
Relative positioning
In the case of relative positioning, the target position is added to the current position. As this does not require a fixed zero
point, homing is not compulsory. However, it is often useful in order to bring the drive to a defined position.
When several relative positioning sequences are added to one another, e.g. for a trimming unit or a conveyor belt, endless
positioning in one direction is possible (chain dimension).
5.3.3
Absolute positioning
In this case, the position target is approached independently of the current position. In order to perform an absolute
positioning process, we recommend referencing (homing) the drive beforehand. In the case of absolute positioning, the target
position is a fixed (absolute) position with regard to the zero point or reference point.
5.3.4
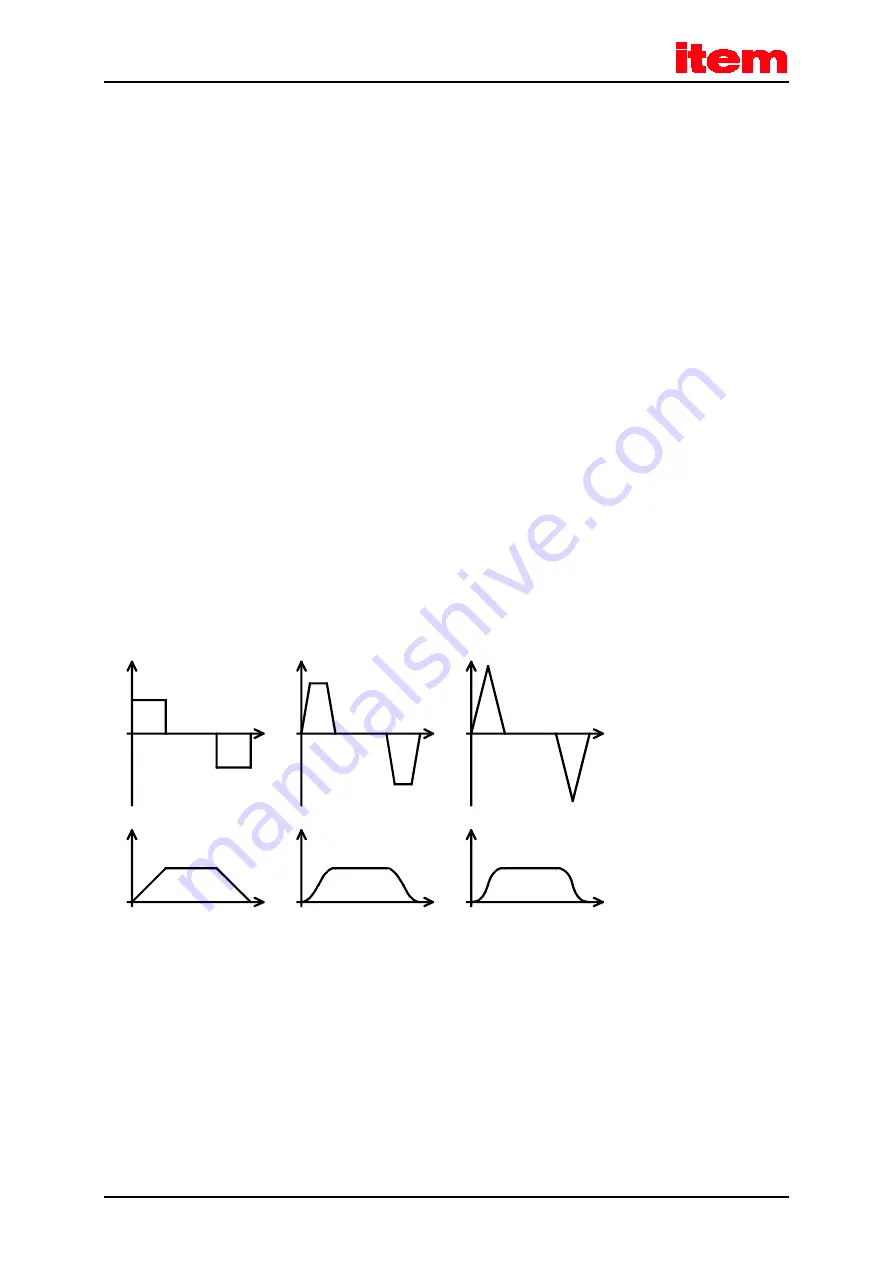
Motion profile generator
In terms of the motion profiles, time-optimal and jerk-limited positioning can be distinguished. In the case of time-optimal
positioning, the maximum set acceleration is used for starting and braking. The drive approaches the target in the shortest
time possible, the velocity profile is trapezoidal, and the acceleration profile is block-shaped. In the case of jerk-limited
positioning, the acceleration profile is trapezoidal and the speed profile is of third order. Since the acceleration changes
steadily, the drive movement is particularly gentle with regard to the mechanical system.
a(t)
a(t)
a(t)
t
t
t
v(t)
t
v(t)
t
v(t)
t
at time optimal
jerk limit
jerk limit
Figure 3:
Motion profiles of the item Servo Positioning Controller C 3-Series
5.3.5
Homing
Every positioning control requires a defined zero at start-up, which is determined by way of a homing operation. The item Servo
Positioning Controller C 3-Series can do this homing on its own. It evaluates several inputs, e.g. the limit switch inputs, as the
reference signal.
















































