Adding the repaired storage system to cluster
1.
After the initialization completes, right-click the cluster, and select
Edit Cluster
. The list of the
storage systems in the cluster should include the ghost IP address.
Add the repaired storage system to the cluster in the spot held by the ghost IP address. See
Table 75 (page 247)
.
2.
Select the ghost storage system (the IP address in the list) and click
Exchange System
.
3.
In the Exchange Storage System window, select the repaired storage system to exchange for
the ghost storage system and then click
OK
.
4.
To ensure that only the repaired storage system goes through the rebuild, verify that the order
of the storage systems in the cluster list matches the original order and then click
OK
.
The storage system returns to its original position in the cluster and volumes in the cluster
proceed to resynchronize.
NOTE:
If you do not arrange the storage systems to match their original order, the data in
the cluster is rebuilt across all the storage systems instead of just the repaired storage system.
This total data rebuild takes longer to complete and increases the chance of a second failure
during this period.
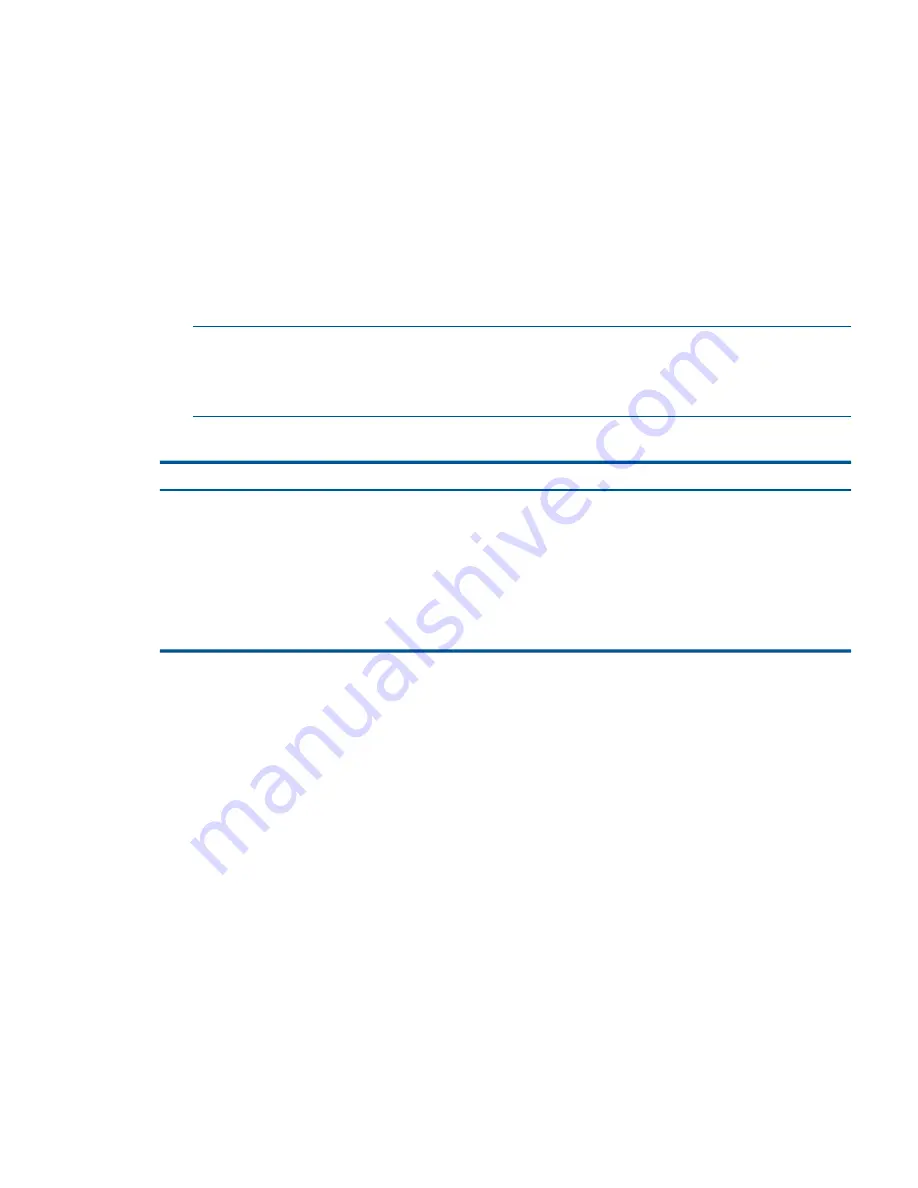
Table 75 Replacing the ghost storage system with the repaired storage system
Storage Systems in Cluster
Before rearranging
•
Storage system A
•
<IP Address>
•
Storage system C
After rearranging
•
Storage system A
•
Storage system B
•
Storage system C
Rebuilding volume data
After the storage system is successfully added back to the cluster, the adjacent storage systems
start rebuilding data on the repaired storage system. To verify progress:
1.
Select the cluster, and select the
Disk Usage
tab.
2.
Verify that the disk usage on the repaired storage system starts increasing.
3.
Verify that the status of the volumes and snapshots is Restriping.
Depending on the usage, it may take anywhere from a few hours to a day for the data to be
rebuilt on the repaired storage system.
Controlling server access
Use the Local Bandwidth Priority setting to control server access to data during the rebuild process:
•
When the data is being rebuilt, the servers that are accessing the data on the volumes might
experience slowness. Reduce the Local Bandwidth Priority to half of its current value for
immediate results.
•
Alternatively, if server access performance is not a concern, raise the Local Bandwidth Priority
to increase the data rebuild speed.
To change local bandwidth priority:
Replacing disks and rebuilding data 247






























