Page 18-43
Pr[Z> z
α
] = 1-
Φ
(z
α
) =
α
, or
Φ
(z
α
) = 1-
α
,
Reject the null hypothesis, H
0
, if z
0
>z
α
, and H
1
: p
1
-p
2
> p
0
, or if z
0
< - z
α
, and
H
1
: p
1
-p
2
<p
0
.
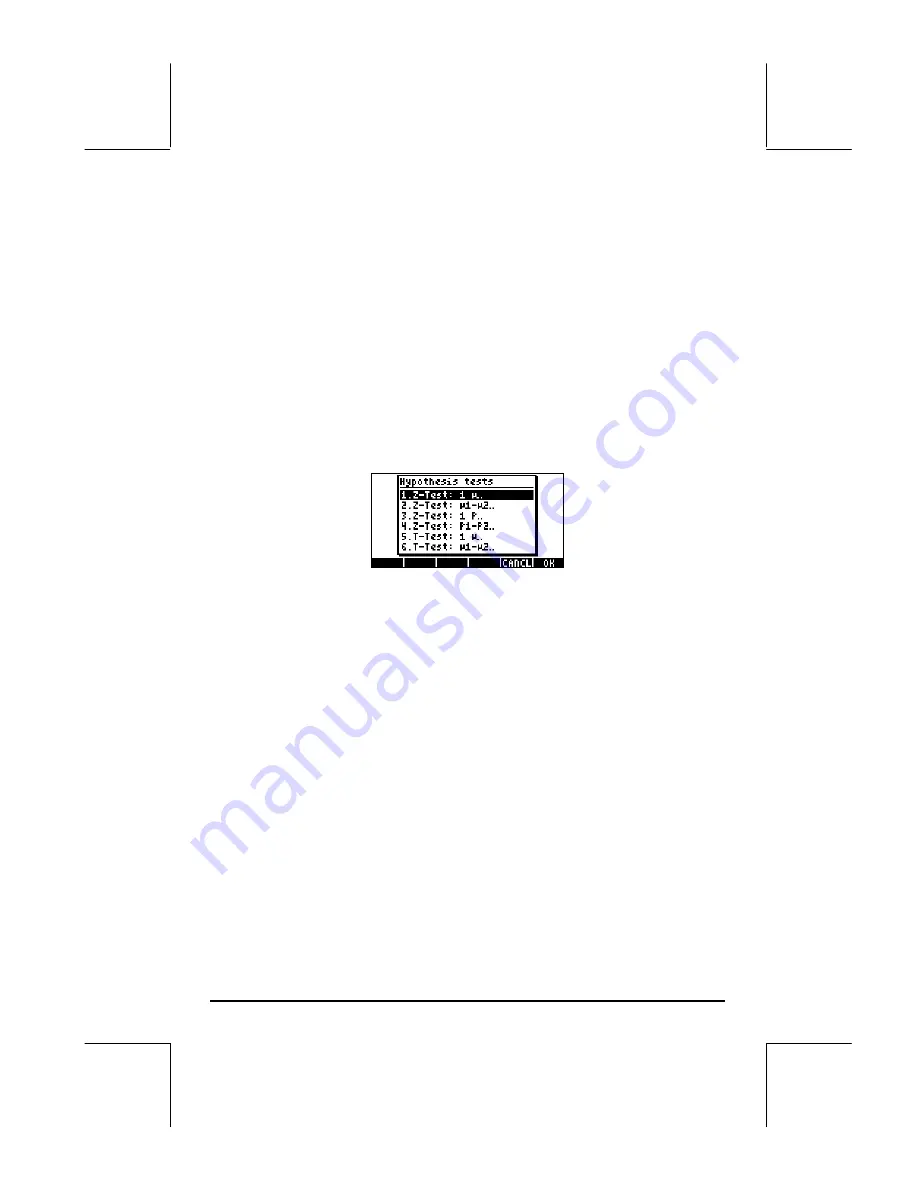
Hypothesis testing using pre-programmed features
The calculator provides with hypothesis testing procedures under application
5. Hypoth. tests..
can be accessed by using
‚Ù——
@@@OK@@@
.
As with the calculation of confidence intervals, discussed earlier, this program
offers the following 6 options:
These options are interpreted as in the confidence interval applications:
1. Z-Test: 1
µ
.: Single sample hypothesis testing for the population mean,
µ
,
with known population variance, or for large samples with unknown
population variance.
2. Z-Test:
µ1−µ2
.: Hypothesis testing for the difference of the population
means,
µ
1
-
µ
2
, with either known population variances, or for large
samples with unknown population variances.
3. Z-Test: 1 p.: Single sample hypothesis testing for the proportion, p, for
large samples with unknown population variance.
4. Z-Test: p
1−
p
2
.: Hypothesis testing for the difference of two proportions,
p
1
-p
2
, for large samples with unknown population variances.
5. T-Test: 1
µ
.: Single sample hypothesis testing for the population mean,
µ
,
for small samples with unknown population variance.
6. T-Test:
µ1−µ2
.: Hypothesis testing for the difference of the population
means,
µ
1
-
µ
2
, for small samples with unknown population variances.






























