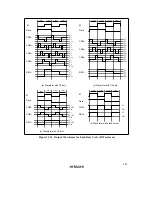
357
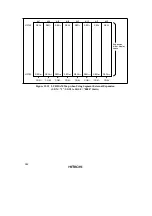
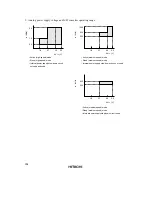
2. Power supply voltage and operating frequency range
16.384
8.192
4.096
1.8
3.6
5.5
V
CC
(V)
ø
SUB
(kHz)
19.2
9.6
4.8
8.0
2.0
5.0
(0.5)
1.0
1.8
2.7
4.5
5.5
V
CC
(V)
V
CC
(V)
ø (MHz)
ø (MHz)
1000
250
625
(7.813)
15.625
1.8
2.7
4.5
5.5
V
CC
(V)
ø (kHz)
2.0
5.0
(0.5)
1.0
1.8 2.7
5.5
V
CC
(V)
ø (kHz)
250
625
(7.813)
15.625
1.8
2.7
5.5
• Active (medium-speed) mode (except A/D converter)
• Sleep (medium-speed) mode (except A/D converter)
• Internal power supply step-down circuit not used
• Active (high-speed) mode
• Sleep (high-speed) mode (except CPU)
• Internal power supply step-down circuit not used
• Active (high-speed) mode
• Sleep (high-speed) mode (except CPU)
• Internal power supply step-down circuit used
• Active (medium-speed) mode (except A/D converter)
• Sleep (medium-speed) mode (except A/D converter)
• Internal power supply step-down circuit used
• Subactive mode
• Subsleep mode (except CPU)
• Watch mode (except CPU)
Figures in parentheses are the minimum operating
frequency of a case external clocks are used.
When using an oscillator, the minimum operating
frequency is ø=1MHz.
Note:
Figures in parentheses are the minimum operating
frequency of a case external clocks are used.
When using an oscillator, the minimum operating
frequency is ø=1MHz.
Note:
Figures in parentheses are the minimum operating
frequency of a case external clocks are used.
When using an oscillator, the minimum operating
frequency is ø=15.625kHz.
Note:
Figures in parentheses are the minimum operating
frequency of a case external clocks are used.
When using an oscillator, the minimum operating
frequency is ø=15.625kHz.
Note: