EN
23
User manual
WF 35
Translation of the original
instructions
RISK OF FIRES AND EXPLOSIONS
Fully shield the welding area, flammable materials should be kept at least 11 metres away.
Fire fighting equipment should be kept close to wherever the welding activities are being undertaken.
Beware the expulsion of hot spatter or sparks, even through cracks, which can cause fires or explosions.
Keep people, flammable objects and pressurised containers at a safe distance.
Welding in closed containers or tubes is to be avoided. If the containers or tubes are open, they must be emptied of all flammable or explosive
materials (oil, fuel, gas residues, etc.).
Grinding work must not be directed towards the source of the welding current or towards any flammable materials.
GAS CYLINDERS
Gas escaping from cylinders can cause suffocation if there is too high a concentration of it in the welding area (ensure good
ventilation).
The machine must be transported in complete safety: gas cylinders must be closed and the welding power source turned off. They
should be stored upright and supported to limit the risk of falling.
Close the cylinder between uses. Beware of temperature variations and exposure to the sun.
The cylinder must not come into contact with flames, arcs, torches, earth clamps or any other sources of heat or ignition.
Be sure to keep it away from electrical and welding circuits. Never weld a pressurised cylinder.
When opening the cylinder valve, keep your head away from the valve and ensure that the gas being used is suitable for the welding process.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
The electrical network used must be earthed. Use the recommended fuse size from the rating plate.
An electric shock can be the source of a serious accident, whether directly or indirectly, or even death.
Never touch live parts connected to the live current, either inside or outside the power source casing unit (torches, clamps, cables, electrodes), as
these items are connected to the welding circuit.
Before opening the device, it is imperative to disconnect it from the mains and wait 2 minutes, so that all the capacitors are discharged.
Do not touch the torch or the electrode holder and the earth clamp at the same time.
If the cables or torches become damaged, they must be replaced by a qualified and authorised person. Measure the cable cross-section according to
the intended application. Always use dry and in-fact clothing to insulate yourself from the welding circuit. Alongside this, wear well-insulated footwear
in all working environments.
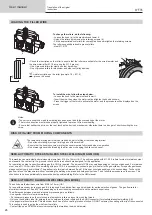
INSTALLATION OF THE REEL AND LOADING OF THE WIRE
Isolation of the welder at the arc in relation to the welding voltage !
Not all the different parts involved in the welding current can be protected against direct human contact. The welder must therefore avoid the risks by
following the relevant safety regulations. Even a contact at low current may take the operator by surprise and cause an incident.
• Make sure protective wear used is dry and in good condition (rubber sole shoes / leather welding gloves without staples or rivets) !
- Avoid direct contact with non-insulated or connecting sockets!
- Always place the welding torch or electrode holder on an insulated support!
Risk of burning at the welding power connection!
If the connectors are not safely locked in place, the connectors and the cables can become hot and cause burns !
• Check the welding connectors daily and lock them in place if needed by turning them to the right.
Risk of electrocution !
If the weld is performed using different processes while the torch and the electrode holder are connected to material, a no-load voltage or welding
voltage is applied to the circuits !
At the beginning of a job and during interruptions, always isolate the torch and the electrode holder !
ELECTRO-MAGNETIC EMISSIONS
An electric current passing through any conductor produces localised electric and magnetic fields (EMF). The welding current
produces an electromagnetic field around the welding circuit and the welding equipment.
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) can interfere with some medical devices, for example pacemakers. Protective measures must be taken for people
with medical implants. For example, restricted access for onlookers or an individual risk assessment for welders.