Revision 5
44
August 2021
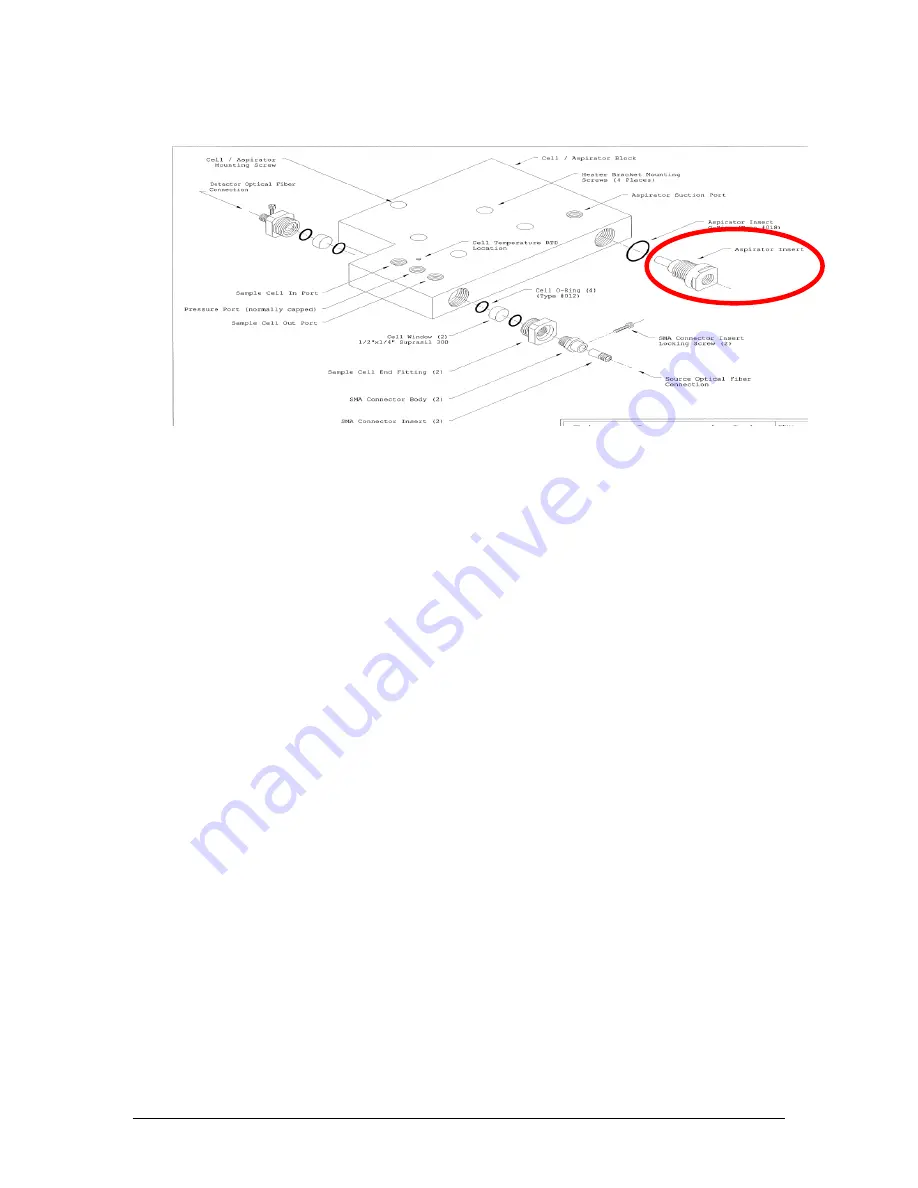
Figure 19: Measurement Cell Block (Exploded View)
The aspirator has a narrow nozzle, and when flowing aspirator drive air passes out of this
nozzle, it expands, causing the pressure on the aspirator suction port to drop. This aspirator
suction port is connected to the outlet of the measurement cell. The design of the analyzer
sample system is such that process sample gas is extracted from near the centre of the
process duct and vented at the wall of the process duct through the same access port.
Ideally, enough aspirator drive air is provided to present a measurement cell outlet pressure
of 2-3" H2O (0.5 to 0.75 kPa) below the process duct pressure. This pressure differential
across the measurement cell draws sample up the
sample probe
, and after the sample is
drawn through the measurement cell it mixes with the aspirator drive air at the aspirator
suction port and is expelled back down the sample probe nozzle and into the process pipe.
In practice, the aspirator drive air flow is adjusted such that the response time from a zero
signal to stable process measurement is less than 30 seconds, though the actual response
time is highly dependent on the sample probe length – the longer the probe, the longer the
response time will be. The adjustment of the aspirator drive air flow is made by monitoring
the amount of time it takes for the displayed concentration values on the analyzer display to
reach stable values after the analyzer has been switched from purge mode to sampling
mode.
An additional consideration that must be made when adjusting the aspirator drive air flow
rate is that if the aspirator drive air flow is set too high, the aspirator air flow will draw a
significant amount of heat out of the measurement cell block, and cause the displayed
cell
temperature
to drop, potentially to below the low cell alarm setpoint. Thus, care must be
taken when adjusting the aspirator drive air flow rate to obtain a balance between stable
temperature control and rapid response time from zero to sample. Typically the aspirator
drive air flow adjust valve is set to two turns from fully closed, but the optimal balance
between temperature control and response time will depend on specific conditions of the
analyzer installation, including but not limited to steam temperature and pressure, ambient
temperature, aspirator drive gas temperature, and the quantity and quality of insulation
applied to the steam lines, sample probe nozzle and ball valve, and analyzer flange.
Summary of Contents for 943-TGS-CE
Page 137: ...Revision 5 137 August 2021 Figure 84 Oven Cabinet Details...
Page 138: ...Revision 5 138 August 2021 Figure 85 Control Cabinet Door Closed...
Page 139: ...Revision 5 139 August 2021 Figure 86 Control Cabinet Door Removed...
Page 140: ...Revision 5 140 August 2021 Figure 87 Power Steam Air Signals Connection Details...
Page 141: ...Revision 5 141 August 2021 Figure 88 AC Wiring Schematic...
Page 142: ...Revision 5 142 August 2021 Figure 89 DC Signals and Wiring Diagram...
Page 143: ...Revision 5 143 August 2021 Figure 90 Flow Diagram...
Page 144: ...Revision 5 144 August 2021 Figure 91 Control and Oven Cabinets Interconnect Wiring...
















































