Chapter 3 - page 1
MC work mode
3. Working with operations or cycles
3. WORKING WITH OPERATIONS OR CYCLES
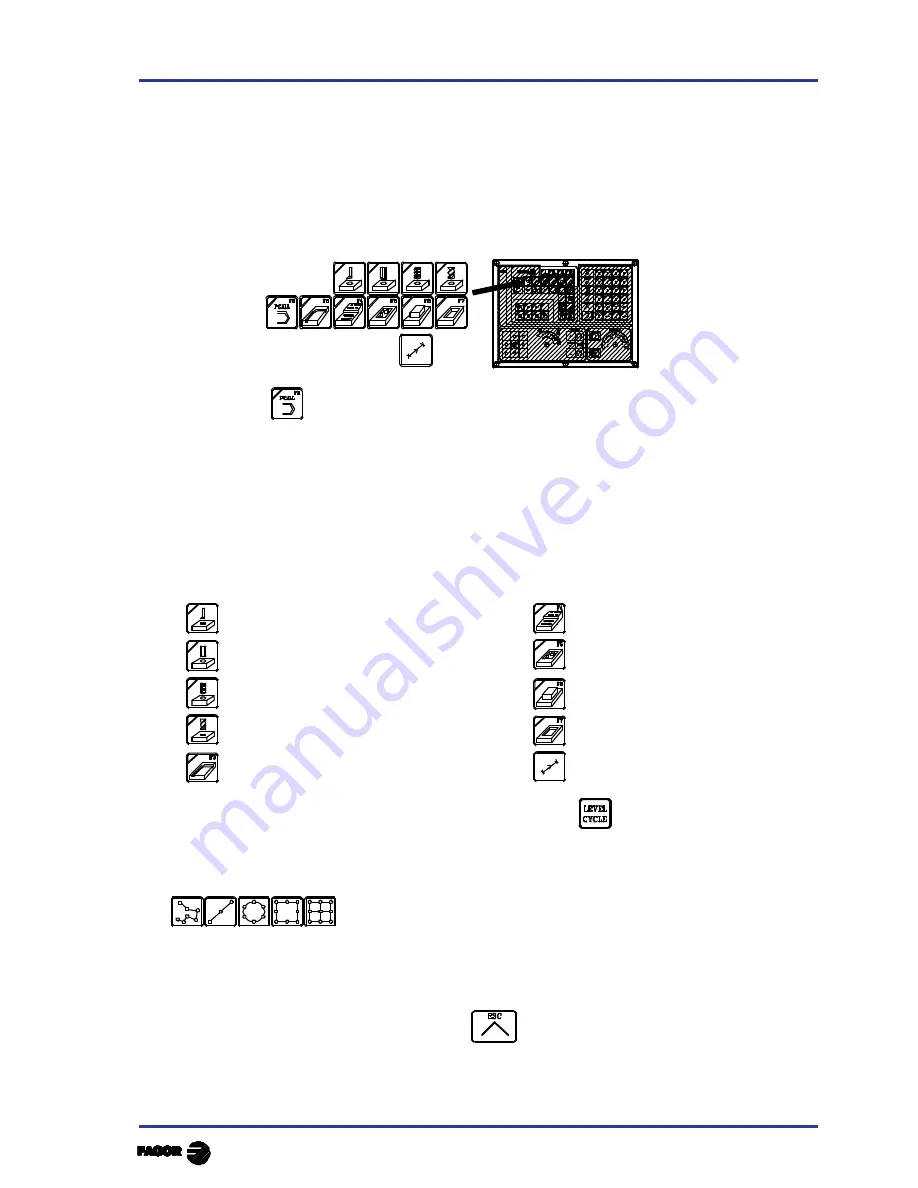
The following keys of the CNC must be used to select the machining operations or cycles:
When pressing
the CNC shows all the user cycles defined by the machine manufacturer using
the WGDRAW application.
The user cycle is edited like any other standard cycle of the MC mode.
Once all the necessary data has been defined, the operator may Simulate or Execute the cycle
just like any other standard cycle of the MC mode.
When pressing any other key, the CNC selects the corresponding machining operation or cycle
changing the display and lighting up the indicator lamp of the key just pressed.
The operations or cycles that can be selected with each one of these keys are the following:
Boring operation (2 levels)
Surface and slot milling
Reaming operation
Pocket with 2D and 3D profile
Tapping operation
Rectangular & circular boss
Drilling (3 levels) & center punching
Rectang. (2) & circular (2) pocket
Profile milling operation (2 levels)
Positioning (2 levels)
When the machining operation or cycle has several levels, the
key must be pressed to select
the desired cycle level:
The Boring , Reaming, Tapping, Drilling and Center punching operations may be carried out at the
position occupied by the tool or they could be associated with a positioning by means of
With this CNC, it is possible to combine ISO-coded blocks with standard and/or user-defined
machining operations to create part-programs as described in the chapter on "Part-program storage".
To deselect the cycle and return to the standard display, press the key corresponding to the selected
cycle (the one with the indicator lamp on) or
Note: the operations or cycles can modify global parameters 150 through 299 (both included).
Summary of Contents for 8040 MC CNC
Page 1: ...REF 0307 SOFT M 7 XX SOFT M 7 1X 8040 CNC NEW FEATURES...
Page 2: ...Page 2 of 2 8040 CNC NEW FEATURES SOFT M 7 XX SOFT M 7 1X...
Page 45: ...User notes NEW FEATURES SOFT M 7 XX Page 41 of 48 8040 CNC...
Page 46: ...User notes NEW FEATURES SOFT M 7 XX Page 42 of 48 8040 CNC...
Page 52: ...User notes NEW FEATURES SOFT M 7 1X Page 48 of 48 8040 CNC...
Page 53: ...Operating Manual MC option Ref 0204 ing...
Page 143: ...Self teaching Manual MC option Ref 0112 ing...
Page 147: ...Chapter 1 Theory on CNC machines...
Page 156: ...Chapter 2 Theory on tools...
Page 164: ...Chapter 3 Hands on training...
Page 186: ...Chapter 4 Automatic Operations...
Page 201: ...Chapter 5 Summary of work cycles...
Page 220: ...Chapter 6 Conversational part programs...
Page 235: ...Appendix I Programming example...
Page 237: ...Self teaching Manual Appendix I Page 3 MC Model Programming example Step 1 Surface milling 1...
Page 239: ...Self teaching Manual Appendix I Page 5 MC Model Programming example Step 3 Rectangular boss 3...
Page 240: ...Self teaching Manual Appendix I Page 6 MC Model Programming example Step 4 Circular pocket 4...
















































