278
7679H–CAN–08/08
AT90CAN32/64/128
Figure 21-6.
ADC Timing Diagram, Auto Triggered Conversion
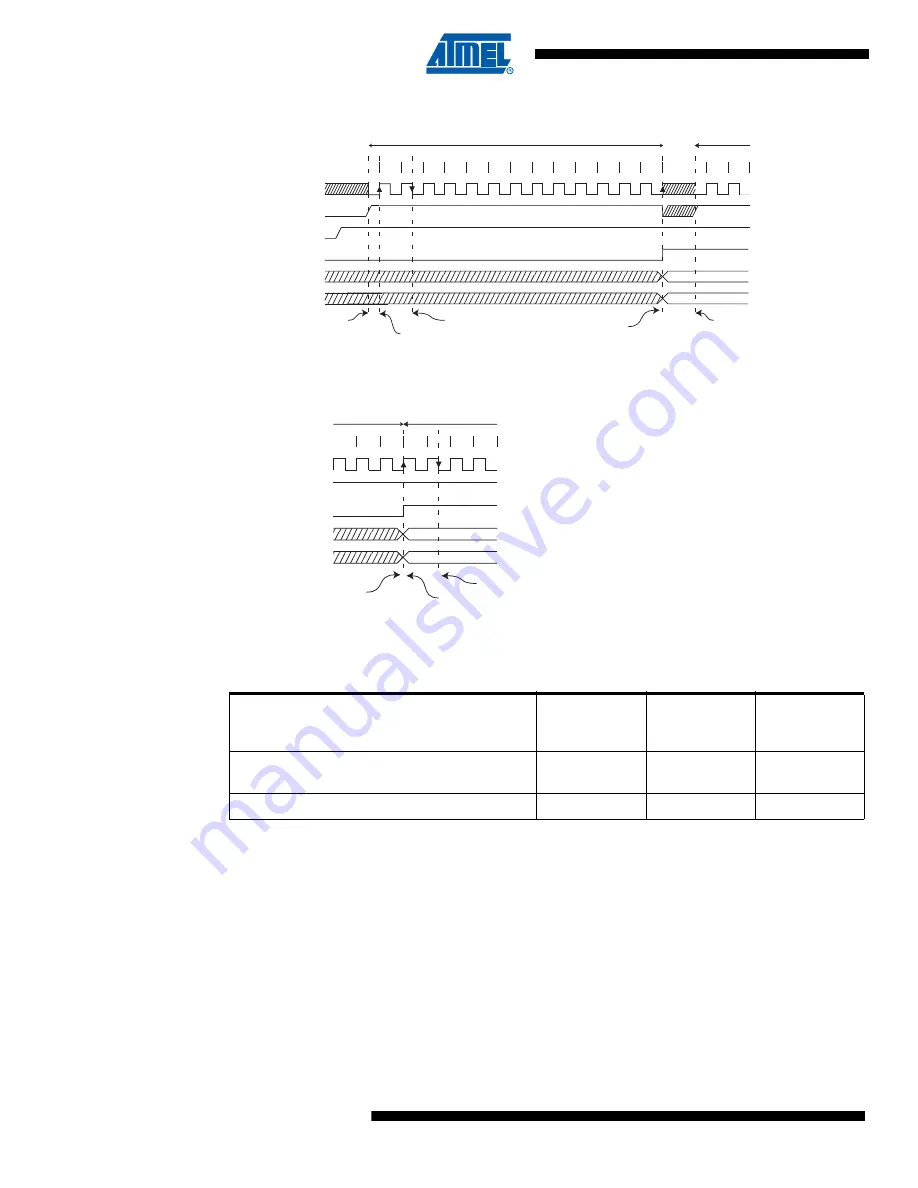
Figure 21-7.
ADC Timing Diagram, Free Running Conversion
21.4.1
Differential Channels
When using differential channels, certain aspects of the conversion need to be taken into
consideration.
Differential conversions are synchronized to the internal clock CK
ADC2
equal to half the ADC
clock frequency. This synchronization is done automatically by the ADC interface in such a way
that the sample-and-hold occurs at a specific phase of CK
ADC2
. A conversion initiated by the
user (i.e., all single conversions, and the first free running conversion) when CK
ADC2
is low will
take the same amount of time as a single ended conversion (13 ADC clock cycles from the next
prescaled clock cycle). A conversion initiated by the user when CK
ADC2
is high will take 14 ADC
clock cycles due to the synchronization mechanism. In Free Running mode, a new conversion is
Table 21-1.
ADC Conversion Time
Condition
First
Conversion
Normal
Conversion,
Single Ended
Auto
Triggered
Conversion
Sample & Hold (Cycles from Start of
Convention)
14.5
1.5
2
Conversion Time (Cycles)
25
13
13.5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Sign and MSB of Result
LSB of Result
ADC Clock
Trigger
Source
ADIF
ADCH
ADCL
Cycle Number
1
2
One Conversion
Next Conversion
Conversion
Complete
Prescaler
Reset
ADATE
Prescaler
Reset
Sample &
Hold
MUX and REFS
Update
11
12
13
Sign and MSB of Result
LSB of Result
ADC Clock
ADSC
ADIF
ADCH
ADCL
Cycle Number
1
2
One Conversion
Next Conversion
3
4
Conversion
Complete
Sample & Hold
MUX and REFS
Update
















































