668
C
HAPTER
48: T
RAFFIC
P
OLICING
, T
RAFFIC
S
HAPING
AND
L
INE
R
ATE
■
Dropping directly — CAR drops the packets that do not "conform to" the
traffic specifications.
■
Forwarding after modifying the packet priority level — The packets with the
estimated result of "partial conformance" are forwarded after they are marked
as the lower priority level flows.
■
Entering the next level of policing — Traffic policing may be stacked level by
level, and each level concerns and polices more specific targets. A downstream
network can receive the estimated result from an upstream network, or it can
be classified according to its own standard.
Traffic policing uses the Token Bucket algorithm, and each service has tokens
which are transmitted at a specified rate. If the reaching speed of the user packets
is faster than the speed at which the tokens are transmitted, it is necessary to take
measures for the data exceeding the specified rate, for example, they are marked
and allowed to pass through the network only when the network is not congested
and they are dropped first when the network is congested. These data packets can
also be dropped directly, which is completely dependent on the agreement and
rules between the operators and users.
Token bucket feature
The token bucket may be regarded as a container that
stores tokens. The system puts tokens into the bucket at the set speed. When the
bucket is full of tokens, the excessive tokens overflow, and the number of the
tokens in the bucket does not increase.
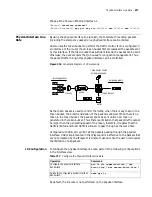
Figure 210
Schematic diagram of packet line classification and traffic policing
Measuring the traffic by the token bucket
Evaluating the traffic specification
by the token bucket is based on whether the number of the tokens in the token
bucket is enough for packet forwarding. If the bucket has sufficient tokens to
forward packets, the traffic does not exceed the specification, otherwise, it
exceeds the specification. Usually, one token is associated with one bit of
forwarding authority.
Three main parameters are used in the evaluation of the traffics:
■
Time Interval: Evaluates the traffic in every other period. This parameter is set
by the system. For every evaluation, if the bucket has sufficient tokens to be
used by one or more packets, it is considered “in conformance”. If the bucket
incoming packets
outgoing packets
Token Bucket
Tokens enter bucket
at the given speed
classify
Discarded
packets
Summary of Contents for 3036
Page 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Page 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Page 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Page 8: ...4 ...
Page 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Page 34: ...30 ...
Page 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Page 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Page 110: ...106 ...
Page 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Page 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Page 168: ...164 ...
Page 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Page 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Page 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Page 320: ...316 ...
Page 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Page 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Page 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Page 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Page 408: ...404 ...
Page 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Page 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Page 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Page 502: ...498 ...
Page 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Page 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Page 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Page 528: ...524 ...
Page 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Page 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Page 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Page 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Page 600: ...596 ...
Page 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Page 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Page 650: ...646 ...
Page 666: ...662 ...
Page 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Page 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Page 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Page 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Page 708: ...704 ...
Page 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...