15
C
ONFIGURING
ISDN P
ROTOCOL
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
■
ISDN Overview
■
Configure ISDN
■
Display and Debug ISDN
■
Typical Configuration Example
■
Fault Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of ISDN
ISDN Overview
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), developed from telephone integrated
digital network (IDN), provides end-to-end digital connection, so as to support
wide range of services (including voice and non-voice services).
ISDN provides the user with a group of standard multifunctional user-network
interfaces. In ITU-T I.412 recommendations, two types of user-network interfaces
are specified: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI). The
bandwidth of BRI is 2B+D, and that of PRI is 30B+D or 23B+D. Here:
■
B channel is a user channel, used to transmit the voice, data and other user
information with the transmission rate 64kbps.
■
D channel is a control channel and used to transmit the common channel
signaling, controlling the calls on B channels of the same interface. The rate of
D channel is 64kbit/s (PRI) or 16kbps (BRI).ITU-T Q.921, the data link layer
protocol of D channel, defines the rules by which the information is exchanged
between layer-2 entities on the user-network interface through D channel.
Meanwhile, it supports the access of layer-3 entity. ITU-T Q.931, the network
layer protocol of D channel, provides methods to establish, maintain and
terminate the network connection between communication application
entities.
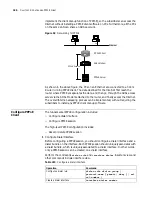
Figure 55
Protocol stack of ISDN D channel
Configure ISDN
ISDN configuration includes:
■
Configure ISDN signaling type
■
Configure QSIG signaling parameters
BRI
PRI
Q.921 LAPD
Q.931
QSIG
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Summary of Contents for 3036
Page 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Page 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Page 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Page 8: ...4 ...
Page 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Page 34: ...30 ...
Page 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Page 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Page 110: ...106 ...
Page 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Page 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Page 168: ...164 ...
Page 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Page 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Page 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Page 320: ...316 ...
Page 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Page 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Page 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Page 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Page 408: ...404 ...
Page 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Page 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Page 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Page 502: ...498 ...
Page 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Page 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Page 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Page 528: ...524 ...
Page 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Page 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Page 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Page 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Page 600: ...596 ...
Page 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Page 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Page 650: ...646 ...
Page 666: ...662 ...
Page 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Page 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Page 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Page 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Page 708: ...704 ...
Page 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...