Configure Frame Relay
247
Note the following:
■
The interface's link layer protocol can be configured to Frame Relay only when
it operates in the synchronous mode.
■
When the interface's link layer protocol is SLIP, the physical attributes of the
interface cannot be modified to synchronous mode. At this time, you should
first modify the link layer protocol of the interface to PPP and then you may
change the interface attribute to synchronous mode.
The Frame Relay interface can send the packet in either of the Frame Relay
formats, while it can recognize and receive packets in both formats. That is, even if
the format of Frame Relay of opposite equipment is different from that of the
local, the equipment at the two ends can communicate with each other as long as
the opposite equipment can recognize the two formats automatically. But when
the opposite equipment can not recognize the two formats automatically, the
Frame Relays of equipment at the two ends must be set to the same format.
2
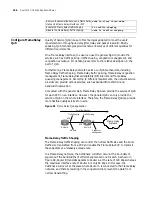
Configure Frame Relay Terminal Type
In Frame Relay, the two sides in communication are classified into user side and
network side. The user side is called DTE, and the network side is called DCE. The
equipment response interface should be configured as DTE or DCE format
according to its location in the network. In Frame Relay networks,
Network-to-Network Interface (NNI) is used between the Frame Relay switches.
In the interface view, perform the following task to configure the type of Frame
Relay interface as DTE, DCE or NNI.
Table 275
Configure Frame Relay interface type
The default type of Frame Relay interface is DTE.
Note the following point: If the terminal type of Frame Relay interface is changed
to DCE or NNI,
fr switching
should be enabled in the system view.
3
Configure Frame Relay LMI Type
The LMI protocol is used to maintain the PVC lists of Frame Relay protocol,
including adding PVC records, deleting the records about disconnected PVCs,
monitoring the change of PVC status, and verifying the link integrity. The 3Com
Router supports three standard LMI protocols: LMI complying with ITU-T Q.933
Appendix A, LMI complying with ANSI T1.617 Appendix D and non-standard LMI.
In the interface view, perform the following task to configure the type of LMI
protocol of Frame Relay interface.
Table 276
Configure Frame Relay LMI protocol type
Operation
Command
Configure Frame Relay interface type
fr interface-type
{
dte |
dce | nni
}
Restore the Frame Relay interface type to the default value
undo fr interface-type
Operation
Command
Configure Frame Relay LMI protocol type
fr lmi type { ansi |
nonstandard | q933a } [
bi-direction ]
Restore the Frame Relay interface LMI protocol type to
default.
undo fr lmi type
Summary of Contents for 3036
Page 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Page 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Page 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Page 8: ...4 ...
Page 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Page 34: ...30 ...
Page 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Page 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Page 110: ...106 ...
Page 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Page 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Page 168: ...164 ...
Page 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Page 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Page 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Page 320: ...316 ...
Page 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Page 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Page 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Page 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Page 408: ...404 ...
Page 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Page 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Page 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Page 502: ...498 ...
Page 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Page 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Page 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Page 528: ...524 ...
Page 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Page 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Page 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Page 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Page 600: ...596 ...
Page 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Page 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Page 650: ...646 ...
Page 666: ...662 ...
Page 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Page 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Page 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Page 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Page 708: ...704 ...
Page 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...