698
C
HAPTER
50: C
ONGESTION
A
VOIDANCE
and it causes the sudden increase and decrease of the network traffic, and the line
traffic always fluctuates between the states of few or none and full.
RED and WRED
RED and WRED can avoid global synchronization of TCP by dropping packets
randomly. When the packets of a TCP connection are dropped, and transmission
slows down, other TCP connections can still send packets at high rates, thus
improving the utilization of the bandwidth.
RED and WRED avoids the TCP global synchronization phenomenon through the
random drop packets--when the packet of a TCP connection is dropped and the
transmission speed is reduced, other TCP connections still have the higher
transmission speeds. Thus, it is always the case that some TCP connection
performs the faster transmission, increasing the use ratio of the line bandwidth.
Both RED and WRED compare between the queue length, and minimum and
maximum thresholds, to perform the drop (this is to set the absolute length of the
queue). It will cause the unfair treatment on the burst data flow and be
disadvantageous for the transmission of the data flow. Therefore, when
comparing the minimum and maximum thresholds, and when dropping, the
average lengths of the queue are adopted (this is to set the relative value of the
comparison between the queue threshold and the average length). The average
length of the queue is the result of the low pass filtering of the queue length, it
reflects the variation trend of the queue, and is not sensitive to the burst change
of the queue length, so as to avoid the unfair treatment on the burst data flows.
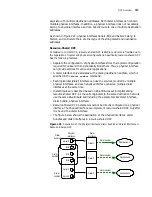
The relationship between WRED and queue mechanism is shown in Figure 223
Figure 223
Schematic diagram of the relationship between WRED and queue mechanism
In the RED class algorithm, a pair of minimum threshold and maximum threshold is
set for each queue, and the following specification is set:
■
When the length of the queue is less than the minimum threshold, no packet is
dropped.
■
When the length of the queue is larger than the maximum threshold, all
incoming packets are dropped.
incoming packets
queue1 weight1
queue2 weight2
classify
outgoing packets
queueN-1 weightN-1
queueN weightN
transmit
queue
interface
¡- ¡-
scheduler
¡- ¡-
WRED drop
Discarded
packets
Summary of Contents for 3036
Page 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Page 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Page 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Page 8: ...4 ...
Page 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Page 34: ...30 ...
Page 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Page 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Page 110: ...106 ...
Page 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Page 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Page 168: ...164 ...
Page 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Page 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Page 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Page 320: ...316 ...
Page 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Page 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Page 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Page 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Page 408: ...404 ...
Page 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Page 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Page 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Page 502: ...498 ...
Page 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Page 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Page 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Page 528: ...524 ...
Page 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Page 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Page 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Page 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Page 600: ...596 ...
Page 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Page 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Page 650: ...646 ...
Page 666: ...662 ...
Page 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Page 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Page 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Page 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Page 708: ...704 ...
Page 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...