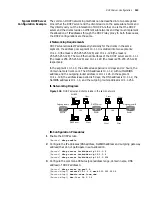
DHCP Server Configuration
335
■
DHCP client logins the network for the first time
If it is the first time for a DHCP client to login to the network, it will establish a
connection with the DHCP server through four stages:
■
Discovering stage. This is the stage when the DHCP client searches the
DHCP servers. The DHCP client broadcasts a DHCP_Discover message to
search the DHCP servers, and every host installed with the TCP/IP suite on
the network will receive this type of broadcast message but only the DHCP
servers respond to it.
■
Offering stage. This is the stage when the DHCP servers offer IP addresses.
Upon receiving the client DHCP_Discover message, the DHCP servers select
an unallocated IP address from the IP address pools for the DHCP client, and
send the DHCP_Offer message containing leased IP address and other
settings to the DHCP client.
■
Selecting stage. This is the stage when the DHCP client selects the IP
address offered by a certain DHCP server. If multiple DHCP servers send the
DHCP_Offer messages to it, the DHCP client will accept only the first
received DHCP_Offer message. Then, it will respond with a DHCP_Request
message by means of broadcasting. This message requests the selected
DHCP server for an IP address.
■
Acknowledgement stage. This is the stage when the DHCP server
acknowledges the offered IP address. Upon receiving the DHCP_Request
message from the DHCP client, the DHCP server sends back a DHCP_ACK
message containing the offered IP address and other settings to the DHCP
client, advising that the offered IP address can be used. Then, the DHCP
client will bind its TCP/IP suite with the network card. Except the server
selected by the DHCP client, other DHCP servers will use their unallocated IP
addresses for the applications of other clients for IP addresses.
■
DHCP client logs into the network again:
■
Once the DHCP client logs into the network correctly, it merely needs to
send the DHCP_Request message containing the IP address allocated
previously (there is no need to send a DHCP_Discover message once again).
■
Upon receiving the DHCP_Request message, the DHCP server will allow the
DHCP client to continue to use the original IP address and will return the
DHCP_ACK message.
■
If the IP address can not be allocated to the DHCP client again (in this case,
the IP address has been allocated to another DHCP client), the DHCP server
will return a DHCP_NAK message. When the DHCP client receives the
DHCP_NAK message, it needs to send a DHCP_Discover message to request
a new IP address.
In addition, you can use the
ipconfig /release_all
command in the
command line on the user PC (that is, the DHCP client) to release the IP
address. In this case, the user PC sends a DHCP_Release message to the DHCP
server. Then, you can use the
ipconfig /renew_all
command on the user PC
to apply for a new IP address. In this case, the user PC sends a DHCP_Discover
message to the DHCP server.
■
DHCP client extends the valid period for leasing the IP address:
■
The dynamic IP address of the DHCP client allocated by the DHCP server
usually has a certain valid leasing period. Upon the expiry, the DHCP server
Summary of Contents for 3036
Page 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Page 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Page 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Page 8: ...4 ...
Page 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Page 34: ...30 ...
Page 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Page 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Page 110: ...106 ...
Page 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Page 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Page 168: ...164 ...
Page 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Page 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Page 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Page 320: ...316 ...
Page 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Page 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Page 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Page 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Page 408: ...404 ...
Page 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Page 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Page 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Page 502: ...498 ...
Page 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Page 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Page 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Page 528: ...524 ...
Page 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Page 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Page 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Page 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Page 600: ...596 ...
Page 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Page 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Page 650: ...646 ...
Page 666: ...662 ...
Page 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Page 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Page 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Page 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Page 708: ...704 ...
Page 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...