IM 701240-02E
0
Main Functions of the SL1400
History Memory
Section 11.1, "Displaying History Waveforms" in the user's manual
When waveforms are being measured, the waveform data stored in the acquisition memory as a result of a trigger being
activated is displayed as waveforms on the SL1400 screen. When triggers are continuously activated and waveforms are ac-
quired, it is impossible to stop the measurement in time when an abnormal waveform appears (newer waveforms appear on
the screen). Normally, abnormal waveforms in the past cannot be displayed. However, by using the history memory function,
the past waveform data (history waveforms) stored in the acquisition memory can be displayed when waveform acquisition is
stopped. A specific history waveform can be displayed.
In addition, waveforms that meet the specified conditions can be searched using the zone search or parameter search func-
tion.
History waveform
(Up to 2000 screens)
Selected Record No. 0
Selected Record No. –25
Specified zone
Detects the waveform
that passed through
the specified zone.
Selected Record No. -28
Selected Record No. 0
Detects waveforms whose
specified waveform parameter
exceeds the specified range.
History waveform
(Up to 2000 screens)
Zone search example
Parameter search example
P-P
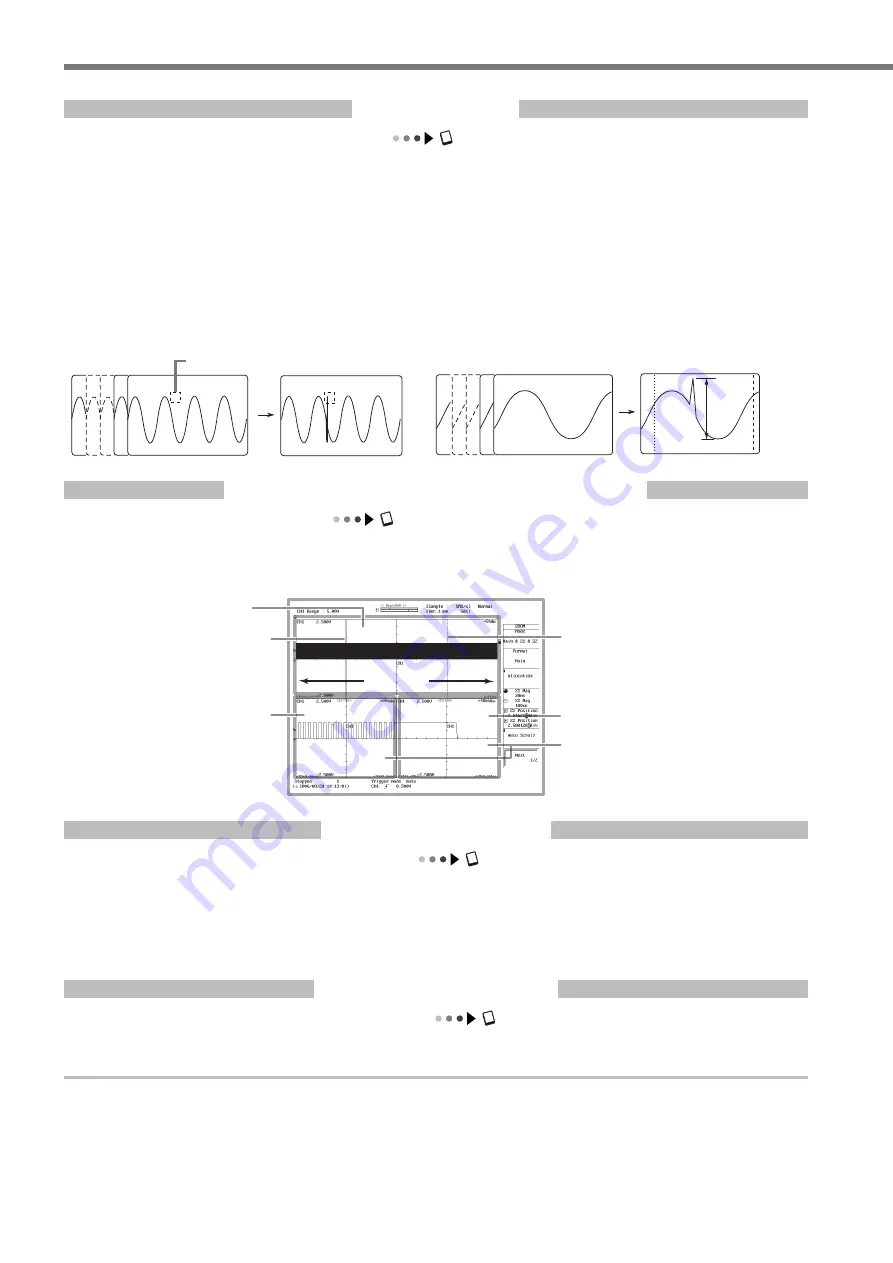
Zooming along the Time (Horizontal) Axis
Section 8.5, "Zooming and Auto Scrolling the Waveform" in the user's manual
The displayed waveform can be expanded along the time (horizontal) axis. Two locations can be zoomed at once. This func-
tion is useful when the waveform acquisition time is set long and you want to observe a particular section of the waveform
closely.
50 MW
Displays zoom waveforms (Z1 and Z2)
of two arbitrary locations.
Zoom box Z1
Zoom box Z2
Zoom waveform window (Z1)
Zoom waveform window (Z2)
Normal waveform window
Displays the entire 50 MW of data
X-Y Waveform Display
Section 8.6, "Displaying X-Y Waveforms" in the user's manual
The level relationship between signals can be observed by assigning the signal level of a specified waveform on the X-axis
(horizontal axis) and the signal level of another waveform (waveform that has the display turned ON) on the Y-axis (vertical
axis). Simultaneous observation of an X-Y waveform and a normal T-Y waveform (waveform using time axis and signal level)
is also possible. Up to 16 X-Y waveforms can be displayed overlapped. The display of multiple X-Y waveforms facilitates the
comparison of the relative phase. This function can be used to evaluate DC motors using Lissajous waveforms.
Waveform Computation
Chapter 10, "Waveform Computation" in the user's manual
Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division (+, –, ×, /), binary computation, FFT (power spectrum), and phase shift (display
or compute by shifting the waveform phase) are possible. Up to eight computations can be set.












































