Supplementary information
18.10 Communication via S7 connections
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
328
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
well as an error in system b, e.g., CP b, will result in a total failure of the communication
between the two systems involved. This can be seen in the preceding figures.
There are no bus system-specific differences in the response to failure.
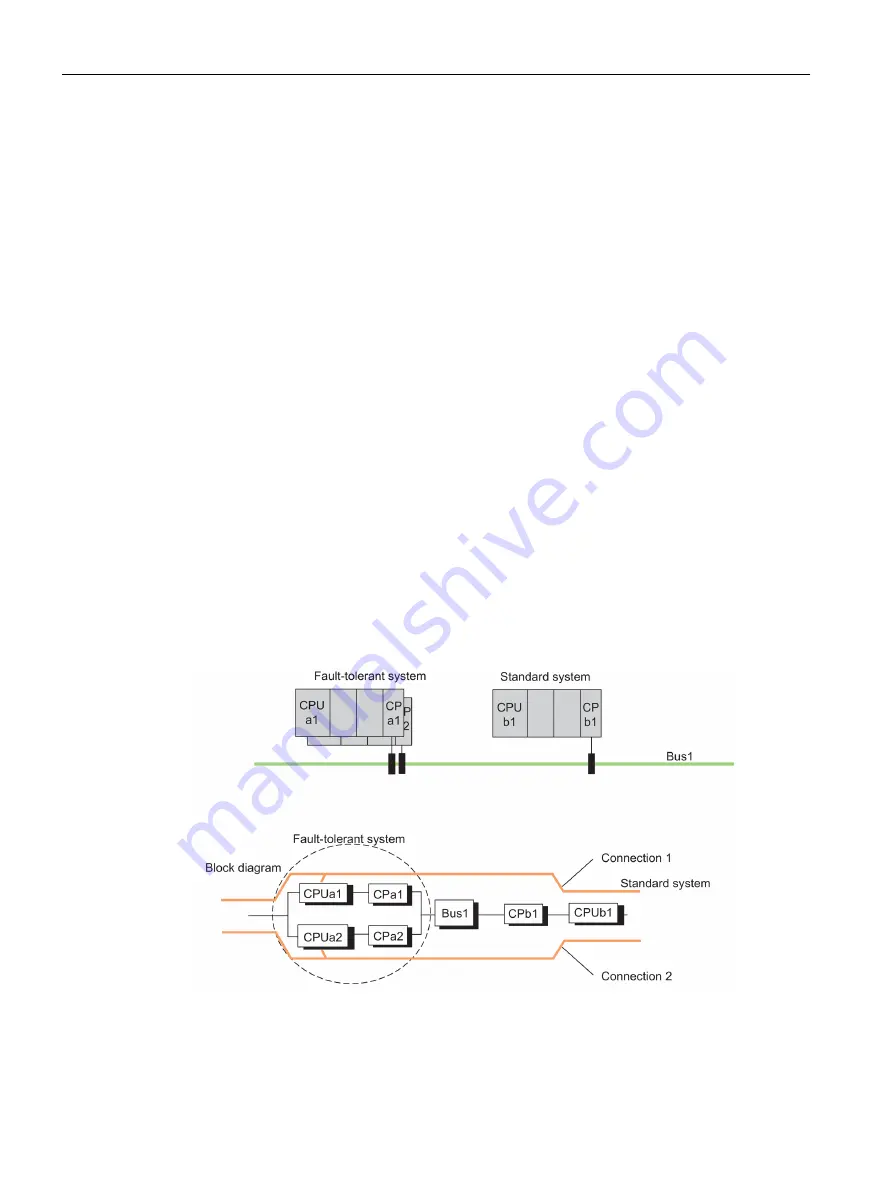
Linking standard and fault-tolerant systems
Driver block "S7H4_BSR": You can link a fault-tolerant system to an S7-400 / S7-300 using
the "S7H4_BSR" driver block. For more information, contact Siemens by e–mail:
function.blocks.industry @siemens.com
Alternative: SFB 15 "PUT" and SFB 14 "GET" in the fault-tolerant system: As an alternative,
use two SFB 15 "PUT" blocks over two standard connections. First call the first block. If
there was no error message when the block executed, the transmission is considered to
have been successful. If there was an error message, the data transmission is repeated via
the second block. If a connection cancelation is detected later, the data is also transferred
again to exclude possible information losses. You can use the same method with an SFB 14
"GET".
If possible, use the mechanisms of S7 communication for communication.
18.10.2
Communication via redundant S7 connections
Availability
Availability compared to using a single bus (see figure below) can be enhanced by using a
redundant system bus and two separate CPs in a standard system.
Figure 18-11 Example of linking standard and fault-tolerant systems in a single bus system
Redundant communication can also be operated with standard connections. For this two
separate S7 connections must be configured in the program in order to implement






























