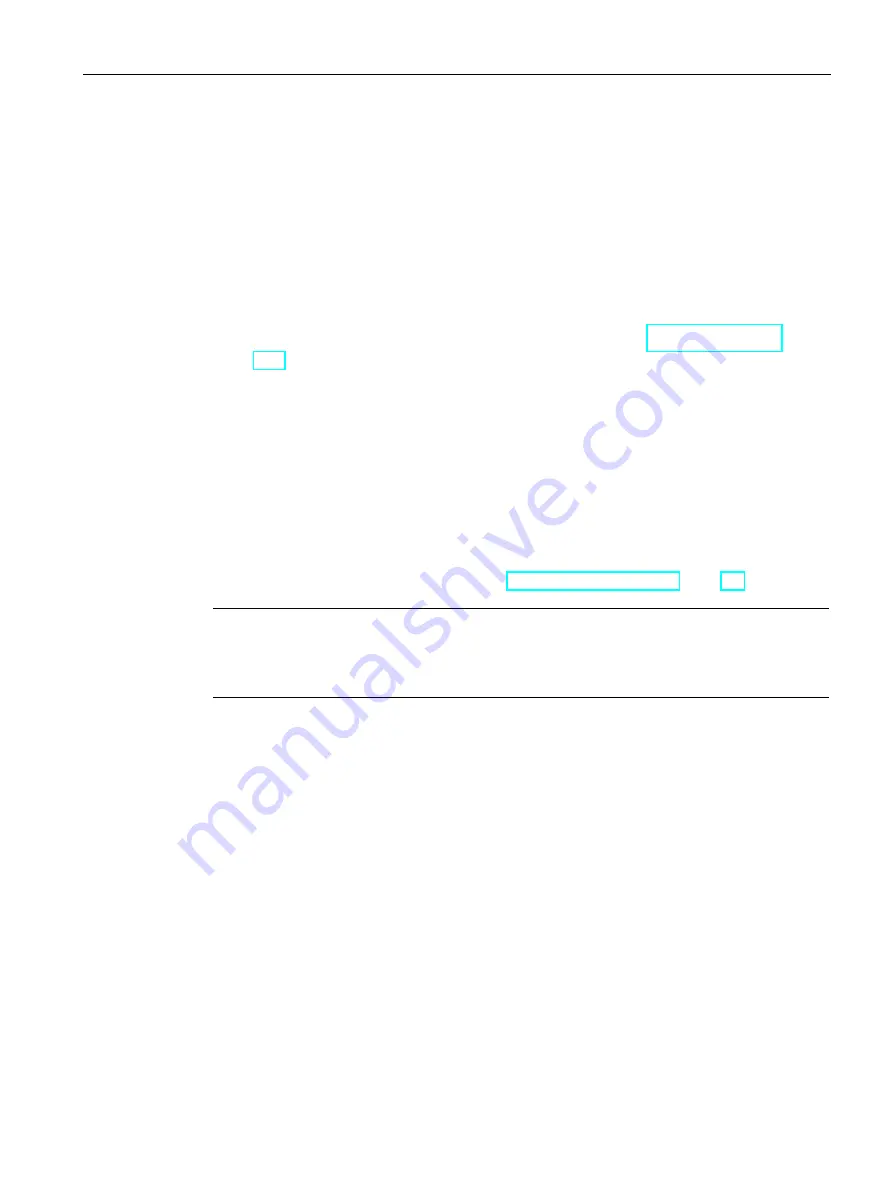
System and operating states of the CPU 410
7.1 CPU 410 operating modes
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
105
7.1.5
LINK-UP and UPDATE modes
The master CPU checks and updates the memory content of the standby CPU before the
fault-tolerant system assumes redundant system mode. This is implemented in two
successive phases: link-up and update.
The master CPU is always in RUN mode and the reserve CPU is in LINK-UP or UPDATE
mode during the link-up and update phases.
In addition to the link-up and update functions, which are carried out to establish redundant
system mode, the system also supports linking and updating in combination with
master/reserve changeover.
For detailed information on connect and updating, refer to section Link-up and update
(Page 119).
7.1.6
ERROR-SEARCH mode
The purpose of ERROR-SEARCH operating state is to find a faulty CPU. The standby CPU
runs the entire self-test; the master CPU remains in RUN. If a hardware fault is detected, the
CPU switches to DEFECTIVE mode. If no fault is detected the CPU is linked up again. The
fault-tolerant system switches back to the redundant system state.
No communication, for example through PG access, is possible with the CPU in
TROUBLESHOOTING mode. The ERROR-SEARCH operating state is indicated by the
flashing RUN and STOP LEDs, see Chapter Status and error displays (Page 41).
Note
If the master CPU changes to STOP during troubleshooting, the troubleshooting is continued
on the standby CPU. However, once troubleshooting is completed, the standby CPU does
not start up again.
The following events will trigger the ERROR-SEARCH operating state:
1.
If there is a one-sided call of OB 121 in redundant operation (at only one CPU), a
hardware fault is assumed and that CPU switches to TROUBLESHOOTING mode. The
other CPU becomes master, if necessary, and continues running in solo operation.
2.
If a checksum error occurs on only one CPU in redundant operation, that CPU switches
to ERROR-SEARCH operating state. The other CPU becomes master, if necessary, and
continues running in solo operation.
3.
If a RAM/PAA comparison error occurs in redundant operation, the backup CPU switches
to TROUBLESHOOTING mode (default response) and the master CPU continues
running in solo mode.
A different response to a RAM/PAA comparison error can be configured (for example
backup CPU switches to STOP).






























