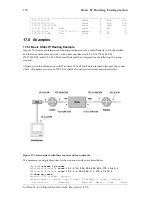
152
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Configuration
18 ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL
(RIP) CONFIGURATION
This chapter provides an overview of the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and describes the tasks
involved in configuring RIP features within SmartWare. For a complete description of the RIP related
commands in this chapter, see Chapter 15, “Interface Mode” in the SmartWare
Command Reference
Guide
.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Introduction
•
Routing Protocol
•
RIP Configuration Task List
18.1 Introduction
RIP is a relatively old but still commonly used interior gateway protocol created for use in small,
homogeneous networks. It is a classical distance-vector routing protocol. RIP is documented in
RFC 1058.
RIP uses broadcast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) data packets to exchange routing information.
The SmartWare software sends routing information updates every 30 seconds, which is termed
advertising.
If a router does not receive an update from another router for 180 seconds or more, it
marks the routes served by the non-updating router as being unusable. If there is still no update after
240 seconds, the router removes all routing table entries for the non-updating router.
The metric that RIP uses to rate the value of different routes is the
hop count.
The hop count is the
number of routers that can be traversed in a route. A directly connected network has a metric of zero;
an unreachable network has a metric of 16. This small range of metrics makes RIP an unsuitable
routing protocol for large networks
A SmartNode that is running RIP can receive a default network via an update from another router
that is running RIP, or the router can source (generate) the default network itself with RIP. In both
cases, the default network is advertised through RIP to other RIP neighbors.
The SmartWare software will send and receive RIP information from the specified interface if the
following conditions are met:
•
The
rip supply
flag for a specific interface is enabled.
•
The
rip listen
flag for a specific interface is enabled.
The default route is learned via a static route and then redistributed into RIP.
RIP sends updates to the specified interfaces. If an interface is not specified, it will not be advertised
in any RIP update.
18.2 Routing Protocol
Routers exchange information about the most effective path for packet transfer between various end
points. There are a number of different protocols, which have been defined to facilitate the exchange
Software Configuration Guide, Revision 1.03
of this information.