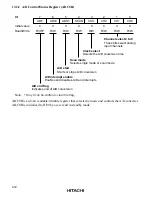
423
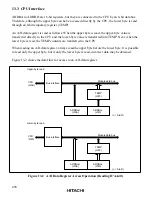
13.5 Interrupts
The A/D converter generates an interrupt (ADI) at the end of A/D conversion. The ADI interrupt
request can be enabled or disabled by the ADIE bit in ADCSR.
13.6
Usage Notes
The following points should be noted when using the A/D converter.
Setting Range of Analog Power Supply and Other Pins:
(1) Analog input voltage range
The voltage applied to analog input pins AN
0
to AN
7
during A/D conversion should be in the
range AV
SS
≤
ANn
≤
AV
CC
.
(2) Relation between AV
CC
, AV
SS
and V
CC
, V
SS
As the relationship between AV
CC
, AV
SS
and V
CC
, V
SS
, set AV
SS
= V
SS
. If the A/D converter is
not used, the AV
CC
and AV
SS
pins must on no account be left open.
If conditions (1) and (2) above are not met, the reliability of the device may be adversely affected.
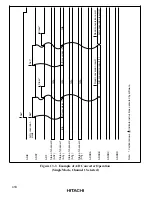
Notes on Board Design: In board design, digital circuitry and analog circuitry should be as
mutually isolated as possible, and layout in which digital circuit signal lines and analog circuit
signal lines cross or are in close proximity should be avoided as far as possible. Failure to do so
may result in incorrect operation of the analog circuitry due to inductance, adversely affecting A/D
conversion values.
Also, digital circuitry must be isolated from the analog input signals (AN
0
to AN
7
), and analog
power supply and reference voltage (AV
CC
) by the analog ground (AV
SS
). Also, the analog ground
(AV
SS
) should be connected at one point to a stable digital ground (V
SS
) on the board.
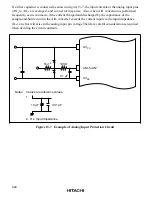
Notes on Noise Countermeasures: A protection circuit connected to prevent damage due to an
abnormal voltage such as an excessive surge at the analog input pins (AN
0
to AN
7
) and analog
power supply (AV
CC
) should be connected between AV
CC
and AV
SS
as shown in figure 13-7.
Also, the bypass capacitors connected to AV
CC
and the filter capacitor connected to AN
0
to AN
7
must be connected to AV
SS
.