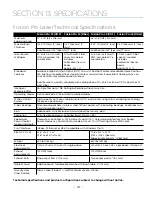
Metal Polishing
Polishing of metals is accomplished by quickly heating up the metal’s surface, changing its color, resulting
in a mirror-like finish. Polishing can be done on just about any metal including, but not limited to, raw
alloys, heat-treated metals, plated metals and precious metals.
For a high-contrast mark, polishing is best done on darker, matte finish metals. Cleaning the surface
prior to processing is recommended as oils, grease and other chemicals can affect the consistency and
finish of the final marks. Dialing in the settings for a polished mark is the most difficult of the three most
popular metal marking techniques. Speed, power and frequency play the biggest role.
• Speed is generally set on the high side, 50-100%, depending on wattage.
• The power is set in the 30-60% range, depending on wattage.
• Frequency is also set on the higher side, typically around the 50-100% range. A higher frequency
setting equates to less power per laser pulse. Too strong of a laser pulse and the laser beam starts
penetrating the metal instead of polishing, resulting in a dull or browning effect.
Focus should be set at zero. Printing resolution is in the range of 300 to 600 DPI but is mostly done at 400
or 600.
Start by determining your base speed, frequency and resolution setting. From there, select a power
setting and start fine tuning by adjusting the power in 1% increments or decrements.
Plastic Marking
The term “plastics” is commonly used to describe various grades and types of polymers. To keep things
simple, we’ll refer to all polymers as plastic. There are many plastics that are compatible with the fiber
laser’s 1062 nm wavelength of light. We refer to these as “engineered plastics” because many were
designed to be laser-etched at some point during the manufacturing life cycle. These plastics are doped
with an additive that results in a contrasting mark when the 1062nm wavelength of light is applied.
There are many other plastics that work just as well as the engineered ones. It’s amazing how many
different plastics we receive for applications testing, most of the time their trade name and chemical
composition aren’t disclosed or are unknown. The guidelines below will help in your quest to provide the
best possible mark.
Most plastics that tend to work on the FiberMark are those that are mold-injected and are physically
hard. Industries where injection molded parts are common include automotive, aerospace, medical
device and general manufacturing, to name a few.
Some of the more common compatible plastics include PET, ABS, polycarbonate and colored delrin.
Some that are more difficult to mark using this wavelength of light include polyethylene, polypropylene
and nylon.
Settings for processing plastics:
• Moderate to fast speed, typically in the 50-80% range.
• Moderate power, generally around the 30-60% range, depending on wattage.
- 194 -
SECTION 12: ENGRAVING MATERIALS
Содержание Fusion Pro 32
Страница 2: ......
Страница 6: ......
Страница 13: ...The following diagrams show the location of each specific label Fusion Pro 32 7 SECTION 1 SAFETY ...
Страница 14: ...Fusion Pro 48 8 SECTION 1 SAFETY ...
Страница 15: ... 9 SECTION 1 SAFETY ...
Страница 18: ......
Страница 28: ......
Страница 60: ......
Страница 98: ......
Страница 108: ......
Страница 132: ......
Страница 162: ......
Страница 184: ......
Страница 202: ......
Страница 214: ......
Страница 216: ......
Страница 242: ......