27
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Router
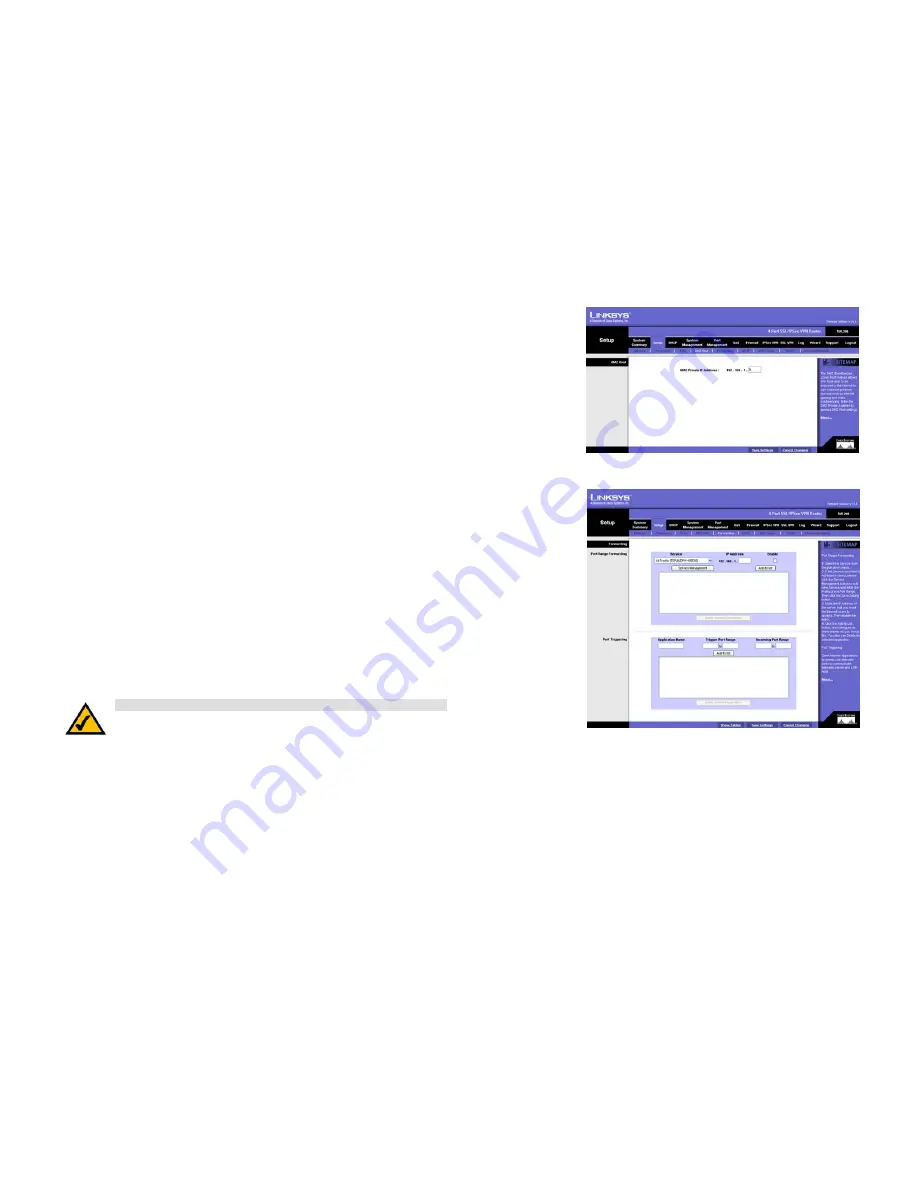
Setup Tab - DMZ Host
4-Port SSL/IPSec VPN Router
Setup Tab - DMZ Host
The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for use of a
special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or video conferencing. Although Port Range Forwarding can
only forward 10 ranges of ports maximum, DMZ hosting forwards all the ports to one PC at the same time.
DMZ Host
DMZ Private IP Address. Enter the local IP address of the computer you want to expose. The default value of
0
deactivates the DMZ Host.
Click the
Save Settings
button to save your change, or click the
Cancel Changes
button to undo the change.
Setup Tab - Forwarding
The
Forwarding
screen allows you to set up port range forwarding and port triggering applications. Port range
forwarding can be used to set up public services or other specialized Internet applications on your network, while
port triggering can be used to set up triggered ranges and forwarded ranges for Internet applications.
Forwarding
Port Range Forwarding
Port forwarding can be used to set up public services on your network. When users from the Internet make
certain requests on your network, the Router can forward those requests to computers equipped to handle the
requests. If, for example, you set the port number 80 (HTTP) to be forwarded to IP address 192.168.1.2, then all
HTTP requests from outside users will be forwarded to 192.168.1.2.
You may use this function to establish a web server or FTP server via an IP gateway. Make sure that you enter a
valid IP address. (You may need to establish a static IP address in order to properly run an Internet server.) For
added security, Internet users will be able to communicate with the server, but they will not actually be
connected. The packets will simply be forwarded through the Router.
Figure 5-22: Setup Tab - DMZ Host
Figure 5-23: Setup Tab - Forwarding
NOTE:
You must disable the Router’s DHCP function to use port forwarding.






























