DS560/DS570 User's Guide - Rev. A04
StorCase Technology, Inc.
Configuration
29
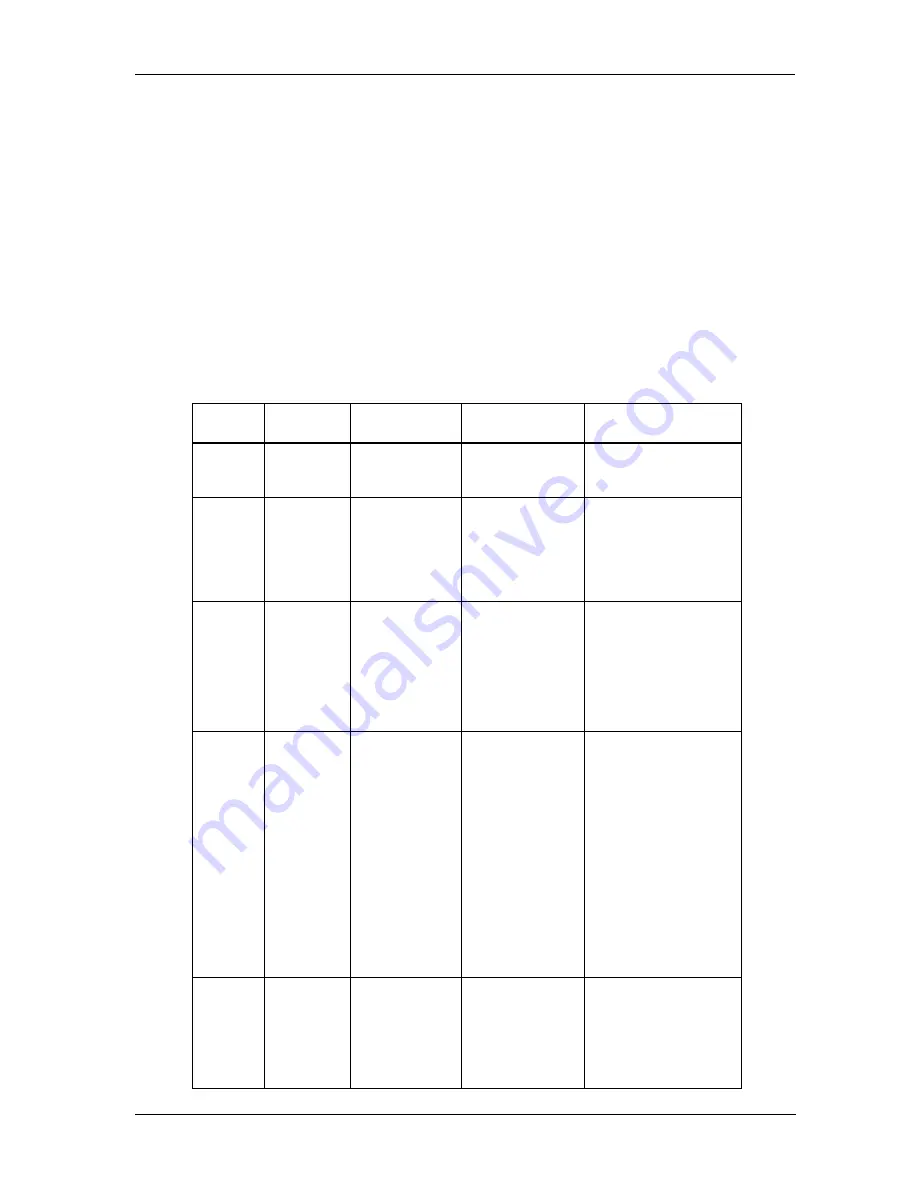
RAID
Level
Minimum #
of Drives
Description
Pros
Cons
RAID 0
2
Data striping
without
redundancy
Highest
performance
No data protection - if
one drive fails, all data
is lost
RAID 1
2
Disk mirroring
Very high
performance and
data protection
Good write
performance
High redundancy costs
- twice the storage
capacity is required
RAID 3
3
Block-level data
striping with
dedicated parity
drive
Excellent
performance for
large, sequential
data requests
Poorly suited for
transaction-oriented
network applications
Single parity drives do
not support multiple,
simultaneous read/write
requests
RAID 5
3
Block-level data
striping with
distributed parity
Best cost and
performance for
transaction-
oriented networks
Very high
performance and
data protection
Supports multiple
simultaneous
read/writes
Can also be
optimized for
large, sequential
requests
Write performance is
slower than RAID 0 or
RAID 1
RAID 10
RAID 0/1
3
Combination of
RAID 0 (data
striping) and
RAID 1
(mirroring)
Highest
performance and
data protection
(can tolerate
multiple drive
failures)
High redundancy costs -
twice the storage
is capacity required
Table 6: RAID Level Comparisons
Array Management
The unique RAID Controller array management firmware utilizes multi-tasking real-time kernel
technology to manage the controller. Additional features are real-time load analysis, online
diagnostics, event logging and broadcasting, and device inventory management.
RAID Levels
The RAID Controller supports RAID levels 0, 0+1, 1, 3, and 5. Depending on the application
that will be used, each RAID level offers a difference in performance, functionality, and fault
tolerance as shown in Table 6.
All manuals and user guides at all-guides.com