1-1
1
ARP Configuration
When configuring ARP, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
z
ARP Overview
z
Configuring ARP
z
Configuring Gratuitous ARP
z
Displaying and Maintaining ARP
ARP Overview
ARP Function
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to resolve an IP address into an Ethernet MAC address
(or physical address).
In a LAN, when a device is to send data to another device, the sending device must know the network
layer address (that is, the IP address) of the destination device. Because IP datagrams must be
encapsulated within Ethernet frames before they can be transmitted over physical networks, the
sending device also needs to know the physical address of the destination device. Therefore, a
mapping between the IP address and the physical address is needed. ARP is the protocol to implement
the mapping function.
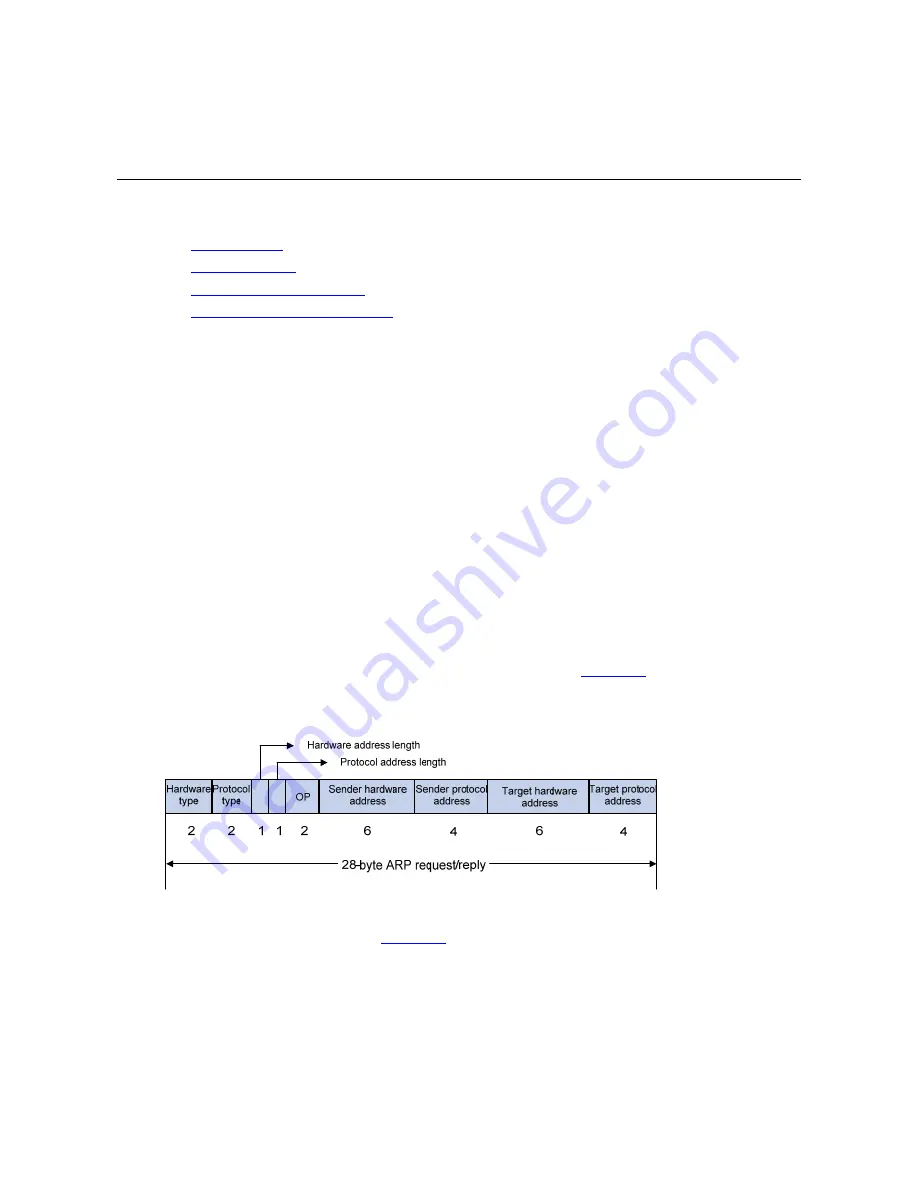
ARP Message Format
ARP messages are classified into ARP requests and ARP replies.
Figure 1-1
shows the format of the
ARP request/reply.
Figure 1-1
ARP message format
The following explains the fields in
Figure 1-1
.
z
Hardware type: This field specifies the hardware address type. The value “1” represents Ethernet.
z
Protocol type: This field specifies the type of the protocol address to be mapped. The hexadecimal
value “0x0800” represents IP.
z
Hardware address length and protocol address length: They respectively specify the length of a
hardware address and a protocol address, in bytes. For an Ethernet address, the value of the
hardware address length field is "6”. For an IP(v4) address, the value of the protocol address length
field is “4”.
















































