CHAPTER 5: SETTINGS
PRODUCT SETUP
M60 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
5-47
5
PRP uses specialized nodes called doubly attached nodes (DANPs) for handling the duplicated frames. DANP devices have
an additional module, called a Link Redundancy Entity (LRE). LRE is responsible for duplicating frames and adding the
specific PRP trailer when sending the frames out on the LAN, as well as making decisions on received frames as to which
one is sent up the OSI stack to the application layer and which one is discarded. LRE is responsible for making PRP
transparent to the higher layers of the stack.
In addition, there is a second type of specialized device used in PRP networks, called RedBox, with the role of connecting
Single Attached Nodes (SANs) to a redundant network.
UR relays implement the DANP functionality. The RedBox functionality is not implemented.
The original standard IEC 62439-3 (2010) was amended to align PRP with the High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR)
protocol. To achieve this, the original PRP was modified at the cost of losing compatibility with the PRP 2010 version. The
revised standard IEC 62439-3 (2012) is commonly referred to as PRP-1, while the original standard is PRP-0. The UR relays
support PRP-1.
The relay implements PRP on two of its Ethernet ports, specifically Ports 2 and 3 of the CPU module. Use the previous
section (network port configuration) to configure PRP.
PRP is purchased as a separate option. If purchased (valid order code), PRP can be enabled in configuration through a
setting available on the network configuration menu, REDUNDANCY, which already has the capability of enabling failover
redundancy. The options on this setting must be changed to accommodate two types of redundancy: failover and PRP.
When REDUNDANCY is set to either failover or PRP, the ports dedicated for PRP (Ports 2 and 3) operate in redundant mode.
In this mode, Port 3 uses the MAC, IP address, and mask of Port 2.
5.3.5.7 IPv4 route table
SETTINGS
PRODUCT SETUP
COMMUNICATIONS
IPv4 ROUTE TABLE 1(6)
A default route and up to six static routes can be configured.
The default route is used as the last choice when no other route towards a given destination is found.
Configure the network IP and subnet settings before configuring the routing settings.
Add and delete static routes
Host routes are not supported at present.
The routing table configuration is available on the serial port and front panel. This is a deliberate decision, to avoid loss of
connectivity when remotely configuring the M60.
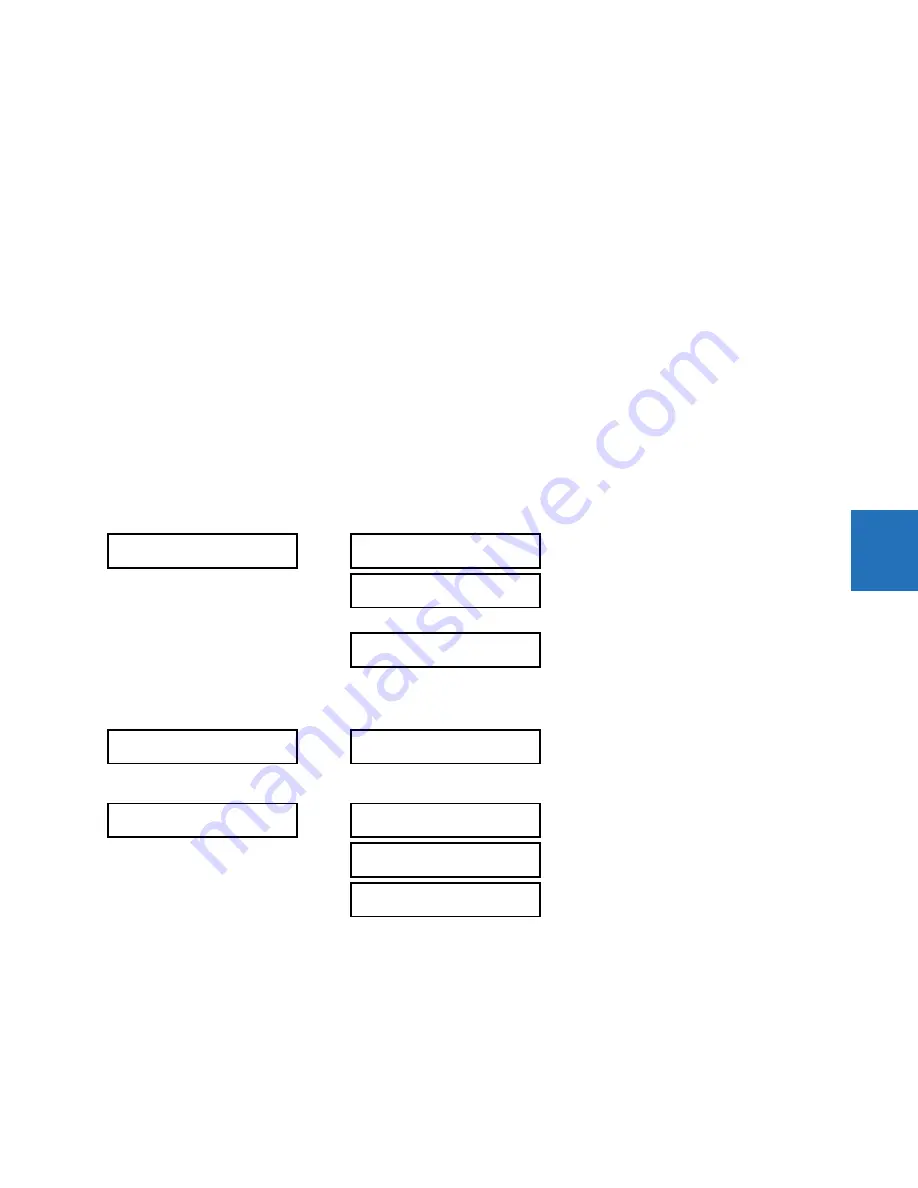
IPv4 ROUTE TABLE
DEFAULT IPv4 ROUTE
IPv4 NETWORK
ROUTE 1
IPv4 NETWORK
ROUTE 6
DEFAULT IPv4 ROUTE
GATEWAY ADDRESS:
127.0.0.1
Range: standard IPV4 unicast address format
IPv4 NETWORK
ROUTE 1
RT1 DESTINATION:
127.0.0.1
Range: standard IPV4 address format
RT1 NET MASK:
255.0.0.0
Range: standard IPV4 subnet mask format
RT1 GATEWAY:
127.0.0.1
Range: standard IPV4 unicast address format
Summary of Contents for M60
Page 9: ...TABLE OF CONTENTS M60 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL ix INDEX ...
Page 10: ...x M60 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS ...
Page 552: ...5 344 M60 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL TESTING CHAPTER 5 SETTINGS 5 ...
Page 660: ...iv M60 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL ABBREVIATIONS ...















































