pCOWeb
+030220966 – rel. 1.1 – 12.12.2017
60
B2 – the DNS provides the IP address of the site.
Once the communications manager has the MAC address of the DNS server, it will send the name www.myserver.com, and the DNS will respond
with the corresponding IP; if the table does not contain the address, the PC will not be able to access www.myserver.com and a warning message
will be displayed. On a PC, the same behaviour can be simulated using the “nslookup” function in Microsoft Windows™:
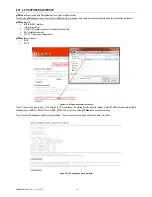
C:\>nslookup www.google.com
Server: ns4.myserver.dns
Address: 10.0.0.14
Response from an untrusted server:
Name: www.l.google.com
Address: 216.239.59.147
Aliases: www.google.com
C – the IP address acquired may not be suitable to contact the server directly: function of the subnet mask.
At this stage, the communications manager checks whether or not it can contact the server’s IP address directly; if not enabled, it will send the
request to contact a network “helper” called the “gateway”, which will forward the message to the recipient (and will do the same for the response);
the gateway can be contacted by the PC as the user will have specified the IP address provided by the network administrator; this IP must be
directly contactable.
Direct contact depends on the combination of the following numbers:
•
IP address of the destination
•
IP address of the personal computer
•
subnet mask of the personal computer
The communications manager, using these three numbers, establishes whether the recipient’s IP address belongs to the range (called the
“subnet”) of IP addresses it is enabled to communicate with, without having to go through the gateway.
The destination IP addresses it can communicate directly with satisfy the following criterion:
the bits of the destination IP address corresponding to those that in the Subnet mask are equal to 1, must have the same value as the
bits of the source IP address
NOTE
The subnet mask cannot have just any value; it must follow a number of rules, including:
•
from the left, at least the first bit must be 1
•
continuing to the right, the first 0 bit will only be followed by 0 bits
Examples
Subnet mask 255. 255. 224. 0
11111111 11111111 11100000 00000000
Source IP 10. 0. 66. 64
00001010 00000000 01000010 01000000
Dest IP 1 (direct) 10. 0. 69. 240
00001010 00000000 01000101 11110000
Dest IP 2 (by gateway) 10. 12. 66. 64
00001010 00001100 01000010 01000000
Dest IP 3 (by gateway) 10. 0. 130. 64
00001010 00000000 11000010 01000000
In other words, the valid range (subnet) for the addresses that can be contacted directly from this PC will be:
ALL DIRECT IP’s RANGE:
Dest IP #1 255. 255. 64. 0
00001010 00000000 01000000 00000000
Dest IP #2 255. 255. 64. 1
00001010 00000000 01000000 00000001
Dest IP #3 255. 255. 64. 2
00001010 00000000 01000000 00000010
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dest IP (#8192) 255. 255. 95. 255
00001010 00000000 01011111 11111111