pCOWeb
+030220966 – rel. 1.1 – 12.12.2017
30
5.3
CONFIGURING CLOCK VIA NTP
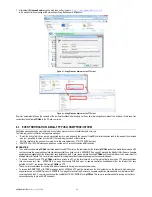
It is possible to configure internal clock to synchronize via a NTP server.
Synchronization can happen only at start or periodically. The address of the NTS server must be configured as shown in
Figure 5.c
.
Figure 5.c - Synchronization via NTP server
NOTE
: The settings will not be valid as soon as they are confirmed;
pCOWeb
needs to be rebooted.
5.4
CONFIGURING VIA BACnet PROTOCOL COMMANDS
It is possible configuring clock
using BACnet protocol commands (e.g. Time Sync/UTC Time Sync in BACset: refer to BACset manual for more information).
When using this method, synchronisation with the time on the controller must be disabled.
5.5
LOGGER AND GRAPHS
pCOWeb
can save the values of max 20 variables sampled at regular time intervals to non-volatile memory (“Logger” function).
pCOWeb
can create also a graph using the vector format SVG and representing in the same graph up to 5 of the logged variables. SVG files can be natively
viewed using Firefox, Chrome, Safari and Edge browsers, while instead Internet Explorer 8 needs an external plug-in (e.g.:
http://www.adobe.com/svg/viewer/install/
)
IMPORTANT: the logging function will not start if the date of the
pCOWeb
is earlier than 01-01-2006. For the date / time settings see sections 5.1, 5.2
and
5.3
on page
29.
IMPORTANT: The range of loggable addresses goes from 0 to 207, even if the ModBus Extended protocol is running.
START OR DISPLAY THE RECORDS
1.
Open the Clock and Logger page (
Figure 5.d
).
2.
Click the “Logger” tab.
The settings are located in the bottom section of the page (
Figure 5.e
sotto); they become active just after the “Submit” confirmation.
Figure 5.d - Opening the Logger and Graph settings
SETTINGS AVAILABLE
Check logger status and free space available: a window is opened that shows the status of the logger (“Running” / “Not Running” / “Logger not
configured or system clock not set correctly”) and the space occupied and free in the non-volatile memory.
Time sample: sample time, common to all the variables.
Compression (.gz): the data files created are .csv; if Compression is enabled, compressed files in .gz format are created, and can be opened
using various decompression tools, for example the “Filzip” freeware,
http://www.filzip.com
(but not with the decompression tool included by
default in the Windows operating system); this is used to save space in the memory, as the data files are made up of highly repetitive data, a
situation that allows significant compression.
Variable 1-20: enable the logging of the variables;
Name: Identifier which will be used in the graphical representation.;
Type: Type of variable (Digital/Analog/Integer);
Index: Numeric identifier of the variable in the database of variables which could be monitored by the monitoring system (index);
Short Description: A short description which will be used in the .csv file to describe the variable;
Group: see below;
Color: Color of the line used to represent the variable in the graph.