DSL LAN Extender 200 User’s Guide
© 2002 Black Box Corporation
Page 12
NOTE:
To turn off bandwidth control in both directions, specify 0 for both the Bandwidth Limit,
Outbound and Inbound fields. To turn off bandwidth control in either the outbound or inbound
direction, specify 0 for the Outbound or Inbound field, depending on the direction you want.
Type <Ctrl-s> to save the new setting.
NOTE:
When using bandwidth control, configure the DSL LAN Extender devic e for the highest data
rate supported by the length and condition of the DSL cable.
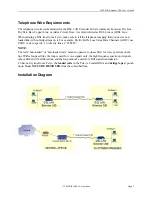
Benefits of Using a DSL LAN Extender as an Internet Access Gateway
You can configure a DSL LAN Extender CP with Bridging disabled and RIP either enabled or disabled.
In this mode, the DSL LAN Extender will act as an Internet access gateway, which treats the local LAN
side as one community. A good example of how this works is in a high-rise apartment building. You
could connect the residents on each floor to a DSL LAN Extender CP device. Each DSL LAN Extender
device, in turn, would connect to a DSL LAN Extender CO.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
This option allows a group of computers connected to a DSL LAN Extender CP device to share a single
IP address, while still allowing the machines to use different private, internal IP addresses. This feature is
useful in situations where users are restricted by a limited (and usually small) number of public IP
addresses assigned by their Internet Service Provider (ISP). For example , by setting the Ethernet Side
Subnet Mask to 255.255.255.0, users have the flexibility of using 254 private, internal IP addresses for
their machines. Yet with NAT turned on, the outside world only sees one, public IP address (the DSL side
IP address) for all the machines.
The NAT option also enhances the security of your network because only a single IP address is presented
to the world, not every computer’s IP address. This makes it harder for hackers to access the computers
on your network.
To turn on the NAT feature, select Y for the NAT Enabled option and enter the NAT IP address (such as
192.168.10.10) and its Net Mask (such as 255.255.255.0).
The CP routing configuration allows public IP addresses to co-exist with the subnet that uses private IP
addresses. When the ISP has assigned more than one public IP address, you can use them for the E-mail
server and/or the HTTP/FTP server. Please see Appendix C for more detailed examples.
Adding Support for Your E-Mail Server and HTTP/FTP Server
The DSL LAN Extender CP device supports the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and Post Office
Protocol 3 (POP3). If you have an e-mail server on your local LAN to handle your organization’s e-mail,
you can configure the DSL LAN Extender CP device to support this server. The advantages of setting up
your own e-mail server are as follows:
•
Reduce Internet traffic across the DSL connection. E-mail messages directed to PCs on the local LAN
aren’t sent across to the remote side. Also, when people on the local LAN side check their e-mail,
their queries are sent to the local e-mail server, instead of over the DSL connection.
•
Provide flexibility in managing e-mail accounts. You can quickly and easily add, delete, or modify e-
mail accounts by yourself.
•
Provide greater security for internal e-mail.
To use an E-mail server, select Y for the E-Mail Server Enabled option. Enter the E-mail server’s IP
address. If you have an HTTP/FTP server, you can also enter its IP address in the next field.