DSL LAN Extender 200 User’s Guide
© 2002 Black Box Corporation
Page 11
To configure the DSL LAN Extender
without using a serial port, please see Appendix D.
Note
: The above tables show the configuration of Case F in Appendix C. (The DSL LAN Extender CP is
NAT enabled, with some using private IP and some using public IP).
Defining the Device IP Address and Subnet Mask
This option lets you define the IP address for the DSL LAN Extender CP device’s connection to your
local LAN. Assign the DSL LAN Extender CP device a valid host IP address that is consistent with the
Ethernet to which it is directly connected. Also, make sure the DSL LAN Extender CP device belongs to
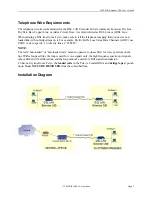
the same subnet as the Ethernet to which it is directly connected. See the illustration at the end of this
section for an example showing IP addresses correctly assigned on a network.
You use this option to specify how many bits in an IP address are considered to be part of the network
portion of the address. For example, the default Ethernet Side Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0, indicates that
24 bits are used for the network portion, leaving 8 bits, or a maximum of 254 node addresses, for this
subnet to use. If you do not expect your organization to require more than 254 nodes in the future, you
should leave the default value for this option.
Defining the Ethernet Side Default Gateway
You use this option to specify the default gateway address of the Internet access router or other router
connected to the DSL LAN Extender’s Ethernet port. Please see Appendix C for examples of setting the
IP parameters for different network environments.
Bandwidth Control
The bandwidth control feature allows you to control the bandwidth allocated for information going out to
the remote side and coming into the local LAN side. Users who mostly download information (from the
Web, for example), would probably want to increase the amount of inbound traffic. On the other hand, if
some users were running their own Web sites, most traffic would flow out from their computers, so they
would probably want to increase the amount of outbound traffic. The inbound and outbound settings
function independently.
Bandwidth control allows ISPs to charge their customers based on the customers’ bandwidth needs. It
also allows ISPs to increase users’ bandwidth allocation quickly and easily, without requiring additional
hardware. In addition, bandwidth control allows users to reconfigure the bandwidth without reconfiguring
the line rate.
To define the desired amount of bandwidth for outbound traffic (that is, traffic flowing from the local
LAN to the remote side), enter the desired bandwidth in the Bandwidth Limit, Outbound field. The
number you enter represents the number of kilobits per second (Kbps). The valid range for this field is 1
to x, where x is the highest data rate supported by the DSL LAN Extender device in its current
configuration.
To define the desired amount of bandwidth for inbound traffic (that is, traffic flowing from the remote
side to the local LAN), enter the desired bandwidth (in Kbps) into the Bandwidth Limit, Inbound field.
The valid range for this field is 1 to x, where x is the highest line rate supported by the DSL LAN
Extender device in its current configuration.