Billion 810VGTX Router
Page | 79
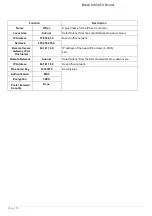
Pre-shared Key: This is for the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol, a string from 4 to 128 characters. Both sides
should use the same key. IKE is used to establish a shared security policy and authenticated keys for services (such as
IPSec) that require a key. Before any IPSec traffic can be passed, each router must be able to verify the identity of its
peer. This can be done by manually entering the pre-shared key into both sides (router or hosts).
Local ID:
Content: Input ID’s information, like domain name
www.ipsectest.com.
Remote ID: Identifier: Input remote ID’s information, like domain name ww.ipsectest.com
Hash Function: It is a Message Digest algorithm which coverts any length of a message into a unique set of bits.
It is widely used MD5 (Message Digest) and SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm) algorithms. SHA1 is more resistant to
brute-force attacks than MD5, however it is slower.
MD5: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 128−bit hash.
SHA1: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 160−bit hash
Encryption: Select the encryption method from the pull-down menu. There are several options, DES, 3DES and AES
(128, 192 and 256). 3DES and AES are more powerful but increase latency.
DES: Stands for Data Encryption Standard, it uses 56 bits as an encryption method.
3DES: Stands for Triple Data Encryption Standard, it uses 168 (56*3) bits as an encryption method.
AES: Stands for Advanced Encryption Standards, you can use 128, 192 or 256 bits as an encryption
method.
Diffie-Hellman Group: It is a public-key cryptography protocol that allows two parties to establish a shared secret
over an unsecured communication channel (i.e. over the Internet). There are three modes, MODP 768-bit, MODP
1024-bit and MODP 1536-bit. MODP stands for Modular Exponentiation Groups.
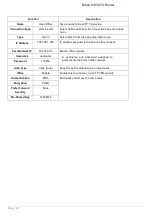
IPSec Proposal: Select the IPSec security method. There are two methods of checking the authentication information,
AH (authentication header) and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload). Use ESP for greater security so that data will
be encrypted and authenticated. Using AH data will be authenticated but not encrypted.
Authentication: Authentication establishes the integrity of the datagram and ensures it is not tampered with in
transmit. There are three options, Message Digest 5 (MD5), Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA1) or NONE. SHA1 is more
resistant to brute-force attacks than MD5, however it is slower.
MD5: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 128−bit hash.
SHA1: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 160−bit hash
Encryption: Select the encryption method from the pull-down menu. There are several options, DES, 3DES, AES
(128, 192 and 256) and NULL. NULL means it is a tunnel with no encryption. 3DES and AES are more powerful but
increase latency.
DES: Stands for Data Encryption Standard, it uses 56 bits as an encryption method.
3DES: Stands for Triple Data Encryption Standard, it uses 168 (56*3) bits as an encryption method.
AES: Stands for Advanced Encryption Standards, you can use 128, 192 or 256 bits as encryption method.
Perfect Forward Secrecy: Choose whether to enable PFS using Diffie-Hellman public-key cryptography to change
encryption keys during the second phase of VPN negotiation. This function of a cryptography protocol is to allow two
parties to establish a shared secret over an unsecured communication channel (i.e. over the Internet). There are three
modes, MODP 768-bit, MODP 1024-bit and MODP 1536-bit. MODP stands for Modular Exponentiation Groups.