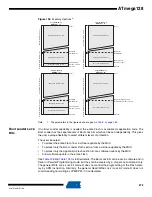
286
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
Memory
Programming
Program and Data
Memory Lock Bits
The ATmega128 provides six Lock bits which can be left unprogrammed (“1”) or can be pro-
grammed (“0”) to obtain the additional features listed in
. The Lock bits can only be
erased to “1” with the Chip Erase command.
Note:
“1” means unprogrammed, “0´means programmed
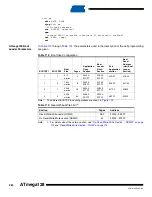
Table 115.
Lock Bit Byte
Lock Bit Byte
Bit No.
Description
Default Value
7
–
1 (unprogrammed)
6
–
1 (unprogrammed)
BLB12
5
Boot lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
BLB11
4
Boot lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
BLB02
3
Boot lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
BLB01
2
Boot lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
LB2
1
Lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
LB1
0
Lock bit
1 (unprogrammed)
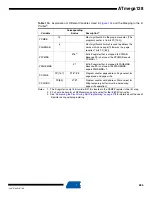
Table 116.
Lock Bit Protection Modes
Memory Lock Bits
Protection Type
LB mode
LB2
LB1
1
1
1
No memory lock features enabled.
2
1
0
Further programming of the Flash and EEPROM is
disabled in Parallel and SPI/JTAG Serial Programming
mode. The Fuse bits are locked in both Serial and Parallel
Programming mode.
3
0
0
Further programming and verification of the Flash and
EEPROM is disabled in Parallel and SPI/JTAG Serial
Programming mode. The Fuse bits are locked in both
Serial and Parallel Programming mode.
BLB0 mode
BLB02
BLB01
1
1
1
No restrictions for SPM or (E)LPM accessing the
Application section.
2
1
0
SPM is not allowed to write to the Application section.
3
0
0
SPM is not allowed to write to the Application section, and
(E)LPM executing from the Boot Loader section is not
allowed to read from the Application section. If interrupt
vectors are placed in the Boot Loader section, interrupts
are disabled while executing from the Application section.
4
0
1
(E)LPM executing from the Boot Loader section is not
allowed to read from the Application section. If interrupt
vectors are placed in the Boot Loader section, interrupts
are disabled while executing from the Application section.
BLB1 mode
BLB12
BLB11