98
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
Modes of
Operation
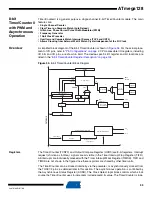
The mode of operation, i.e., the behavior of the Timer/Counter and the output compare pins, is
defined by the combination of the Waveform Generation mode (WGM01:0) and Compare Output
mode (COM01:0) bits. The Compare Output mode bits do not affect the counting sequence,
while the Waveform Generation mode bits do. The COM01:0 bits control whether the PWM out-
put generated should be inverted or not (inverted or non-inverted PWM). For non-PWM modes
the COM01:0 bits control whether the output should be set, cleared, or toggled at a compare
match (
See “Compare Match Output Unit” on page 97.
).
For detailed timing information refer to
“Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams” on page 102
Normal Mode
The simplest mode of operation is the normal mode (WGM01:0 = 0). In this mode the counting
direction is always up (incrementing), and no counter clear is performed. The counter simply
overruns when it passes its maximum 8-bit value (TOP = 0xFF) and then restarts from the bot-
tom (0x00). In normal operation the Timer/Counter overflow flag (
TOV0
) will be set in the same
timer clock cycle as the TCNT0 becomes zero. The
TOV0
flag in this case behaves like a ninth
bit, except that it is only set, not cleared. However, combined with the timer overflow interrupt
that automatically clears the
TOV0
flag, the timer resolution can be increased by software. There
are no special cases to consider in the normal mode, a new counter value can be written
anytime.
The output compare unit can be used to generate interrupts at some given time. Using the out-
put compare to generate waveforms in normal mode is not recommended, since this will occupy
too much of the CPU time.
Clear Timer on
Compare Match (CTC)
Mode
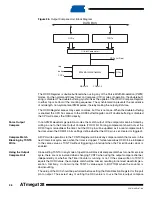
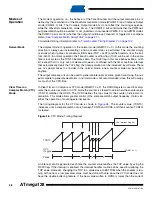
In Clear Timer on Compare or CTC mode (WGM01:0 = 2), the OCR0 Register is used to manip-
ulate the counter resolution. In CTC mode the counter is cleared to zero when the counter value
(TCNT0) matches the OCR0. The OCR0 defines the top value for the counter, hence also its
resolution. This mode allows greater control of the compare match output frequency. It also sim-
plifies the operation of counting external events.
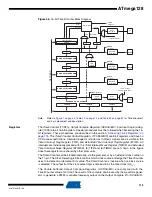
The timing diagram for the CTC mode is shown in
. The counter value (TCNT0)
increases until a compare match occurs between TCNT0 and OCR0, and then counter (TCNT0)
is cleared.
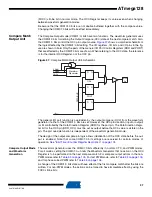
Figure 38.
CTC Mode, Timing Diagram
An interrupt can be generated each time the counter value reaches the TOP value by using the
OCF0 flag. If the interrupt is enabled, the interrupt handler routine can be used for updating the
TOP value. However, changing the TOP to a value close to BOTTOM when the counter is run-
ning with none or a low prescaler value must be done with care since the CTC mode does not
have the double buffering feature. If the new value written to OCR0 is lower than the current
TCNTn
OCn
(Toggle)
OCn Interrupt Flag Set
1
4
Period
2
3
(COMn1:0 = 1)